Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
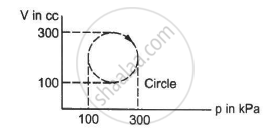
उत्तर
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
Since internal energy depends only on the initial and final points and for a cyclic process, initial and final points are the same, change in internal energy of the system during this process will be zero.
⇒ ΔU = 0
⇒ ΔQ = ΔW
Heat absorbed = Work done
Work done = Area under the graph in the given case
Thus,
Heat absorbed = Area of the circle
Diameter of the circle = 300 - 100 = 200
Heat absorbed = π"> × 104 × 10−6 × 103 J
= 3.14 × 10 = 31.4 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for Isothermal Process
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
120 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose internal energy change is 60 J, then the amount of external work done is ____________.
For a particular reaction, the system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.5 kJ of work on its surrounding. What will be the change in internal energy of the system?
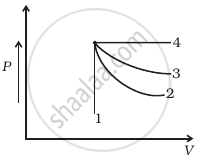
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
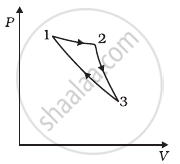
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Write a short note on isobar.
