Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
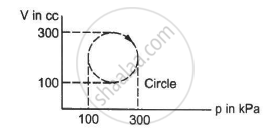
Solution
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
Since internal energy depends only on the initial and final points and for a cyclic process, initial and final points are the same, change in internal energy of the system during this process will be zero.
⇒ ΔU = 0
⇒ ΔQ = ΔW
Heat absorbed = Work done
Work done = Area under the graph in the given case
Thus,
Heat absorbed = Area of the circle
Diameter of the circle = 300 - 100 = 200
Heat absorbed = π"> × 104 × 10−6 × 103 J
= 3.14 × 10 = 31.4 J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
For an Isochoric process
The process, in which no heat enters or leaves the system, is termed as ____________.
For a particular reaction, the system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.5 kJ of work on its surrounding. What will be the change in internal energy of the system?
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
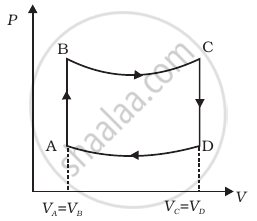
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
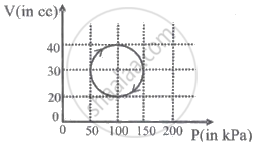
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
200g water is heated from 40°C to 60°C. Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to ______.
(Given specific heat of water = 4184 J/kgK)
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
In an adiabatic process, ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
What is Isobaric process?
A monoatomic gas at 27°C is adiabatically compressed to 80% of its initial volume. Find the final temperature of the gas.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
