Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For an Isochoric process
Options
∆U = 0
∆V = 0
∆P = 0
Q = 0
Solution
∆V = 0
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
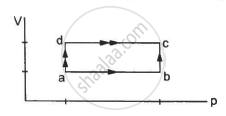
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
Calculate the increase in the internal energy of 10 g of water when it is heated from 0°C to 100°C and converted into steam at 100 kPa. The density of steam = 0.6 kg m−3. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and the latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.25 × 10 6J kg−1.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
"The mass and energy both are conserved in an isolated system", is the statement of ______.
The process, in which no heat enters or leaves the system, is termed as ____________.
Based on first law of thermodynamics which of the following is correct.
120 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose internal energy change is 60 J, then the amount of external work done is ____________.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is ______.
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
- dU = 0
- dQ= 0
- dQ = dU
- dQ = dW
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
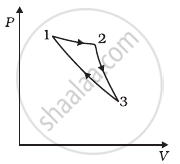
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
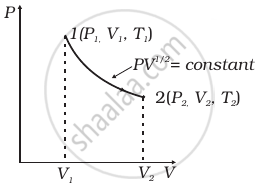
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
One mole of an ideal gas is allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from a temperature of 27°C. If the work done during the process is 3 kJ, the final temperature will be equal to ______.
(Cv = 20 JK−1)
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
One mole of an ideal gas is initially kept in a cylinder with a movable frictionless and massless piston at pressure of 1.01MPa, and temperature 27°C. It is then expanded till its volume is doubled. How much work is done if the expansion is isobaric?
In an adiabatic process, ______.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
A monoatomic gas at 27°C is adiabatically compressed to 80% of its initial volume. Find the final temperature of the gas.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
Write a short note on isobar.
