Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
- dU = 0
- dQ= 0
- dQ = dU
- dQ = dW
Solution
a and d
Explanation:
First Law of Thermodynamics: It is a statement of conservation of energy in a thermodynamical process.
According to it, heat given to a system (∆Q) is equal to the sum of the increase in its internal energy (AIT) and the work done (AW) by the system against the surroundings.
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
According to the first law of thermodynamics.
∆AQ = ∆U + ∆W but ∆U ∝ ∆T
∆U = 0 .....[As ∆T = 0]
∆Q = ∆W, i.e., heat supplied in an isothermal change is used to do work against external surroundings.
or if the work is done on the system then an equal amount of heat energy will be liberated by the system
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
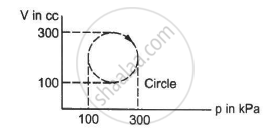
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
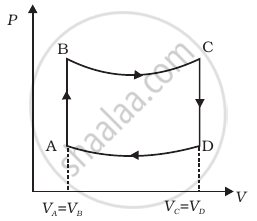
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
