Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
- dU = 0
- dQ= 0
- dQ = dU
- dQ = dW
उत्तर
a and d
Explanation:
First Law of Thermodynamics: It is a statement of conservation of energy in a thermodynamical process.
According to it, heat given to a system (∆Q) is equal to the sum of the increase in its internal energy (AIT) and the work done (AW) by the system against the surroundings.
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
According to the first law of thermodynamics.
∆AQ = ∆U + ∆W but ∆U ∝ ∆T
∆U = 0 .....[As ∆T = 0]
∆Q = ∆W, i.e., heat supplied in an isothermal change is used to do work against external surroundings.
or if the work is done on the system then an equal amount of heat energy will be liberated by the system
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
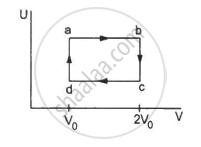
Figure shows the variation in the internal energy U with the volume V of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas in a cyclic process abcda. The temperatures of the gas at b and c are 500 K and 300 K respectively. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas during the process.
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
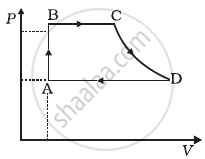
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
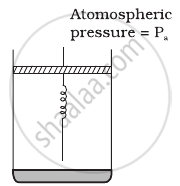
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
An electric appliance supplies 6000 J/min heat to the system. If the system delivers a power of 90 W. How long it would take to increase the internal energy by 2.5 × 103 J?
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
