Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
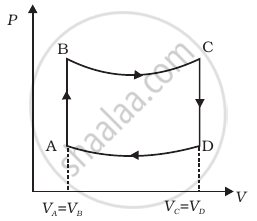
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
Solution
a. For process AB (which is the isochoric process), volume is constant.
So, dV = 0
⇒ dW = 0
dQ = dU + dW = dU
⇒ dQ = dU = Change in internal energy
Hence, in this process heat supplied is utilised to increase, the internal energy of the system.
b. For the process CD (which is also an isochoric process), volume is constant but the pressure decreases. Hence, temperature also decreases (because PαT) so heat is given to the surroundings.
c. To calculate work done by the engine in one cycle, we calculate work done in each part separately.
(i) `W_(AB) = int_A^B PdV` = 0
(ii) `W_(CD) = int_C^D PdV` = 0 ....(As V is constant, dV = 0)
(iii) `W_(BC) = int_B^C PdV`
= `K int_B^C (dV)/(V^γ)`
= `K int_(V_B)^(V_C) V^-γ dV`
= `K/(1 - γ) [V^(1 - γ)]_(V_B)^(V_C)`
= `(K[V_C^(1 - γ) - V_B])/(1 - γ)` .....(PVγ = K for an adiabatic change)
= `([(P_CV_C^γ)(V_C^(1 - γ)) - (P_BV_B^γ)(V_B^(1 - γ))])/((1 - γ))`
Similarly, `W_(DA) = int_(V_D)^(V_A) PdV`
= `1/((1 - γ)) (P_AV_A - P_DV_D)` ......[∵ BC is an adiabatic process]
Since B and C lies on adiabatic curve BC,
∴ `P_BV_B^γ = P_CV_C^γ`
`P_C = P_B(V_B/V_C)^γ`
= `P_B(1/2)^γ`
= `2^(-γ)P_B`
Similarly, `P_D = 2^(-γ)P_A`
Total work done by the engine in one cycle ABCDA
`W = W_(AB) + W_(BC) + W_(CD) + W_(DA) = W_(BC) + W_(DA)`
= `((P_CV_C - P_BV_B))/(1 - γ) + ((P_AV_A - P_DV_D))/(1 - γ)`
`W = 1/(1 - γ) [2^(-γ) P_B (2V_B) - P_BV_B + P_AV_A - 2^(-γ) P_B (2V_B)]`
= `1/(1 - γ) [P_AV_B (2^(-γ + 1) - 1) - P_AV_A (2^(-γ + 1) - 1)`
= `1/(1 - γ) (2^(1 - γ) - 1) (P_B - P_A)V_A`
= `3/2 [1 - (1/2)^(2/3)](P_B - P_A)V_A`
d. Heat (Q) is supplied to the engine only from A to B. Thus Q = ΔQAB = ΔUAB = nCVΔT
= `3/2 R(T_B - T_A)` .....[As CV = (3/2)R and ΔT = TB – TA]
= `P_CV_C^γ = P_BV_B^γ`,
`P_C = P_B(V_B/V_C)^γ`
= `P_B(1/2)^γ`
= `P_B2^-γ` .....(As VB/VC = 1/2)
Thus, `P_CV_C^γ = (P_B2^-γ)(2V_B) = 2^(1 - γ)P_BV_B`
= `3/2 (P_BV_B - P_AV_A)`
= `3/2 (P_B - P_A)V_A` .....(PV = RT and VB = VA)
The efficiency of the engine,
η = `W/Q = (3/2 [1 - (1/2)^(2/3)] (P_B - P_A)V_A)/(3/2 (P_B - P_A)V_A)`
= `[1 - (1/2)^(2/3)]`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
The process, in which no heat enters or leaves the system, is termed as ____________.
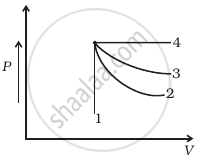
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
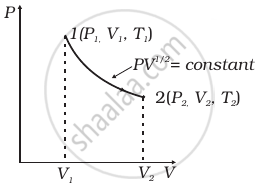
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
In an adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the initial pressure was 1.013 × 105 Pa, the initial volume was 22.4 L, the final pressure was 3.191 × 104 Pa and the final volume was 44.8 L. Find the work done by the gas on its surroundings. Taken `γ = 5/3`.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
A monoatomic gas at 27°C is adiabatically compressed to 80% of its initial volume. Find the final temperature of the gas.
