Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For an Isochoric process
पर्याय
∆U = 0
∆V = 0
∆P = 0
Q = 0
उत्तर
∆V = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
120 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose internal energy change is 60 J, then the amount of external work done is ____________.
For a particular reaction, the system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.5 kJ of work on its surrounding. What will be the change in internal energy of the system?
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
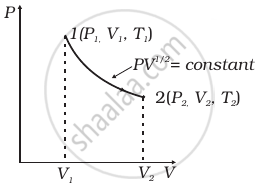
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
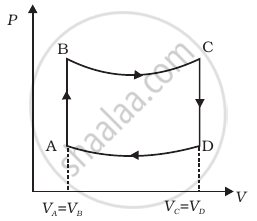
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
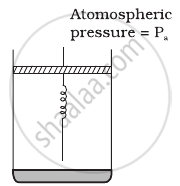
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
200g water is heated from 40°C to 60°C. Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to ______.
(Given specific heat of water = 4184 J/kgK)
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
What is true for an adiabatic process?
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
Write a short note on isobar.
