Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the increase in the internal energy of 10 g of water when it is heated from 0°C to 100°C and converted into steam at 100 kPa. The density of steam = 0.6 kg m−3. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and the latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.25 × 10 6J kg−1.
उत्तर
Given:-
Mass of water, m = 10 g = 0.01 kg
Pressure, P = 105 Pa
Specific heat capacity of water, c = 1000 J/Kg °C
Latent heat, L = 2.25 × 106 J/Kg
∆ t = Change in temperature of the system = 100°C = 373 K
∆Q = Heat absorbed to raise the temperature of water from 0°C to 100°C + Latent heat for conversion of water to steam
∆Q = \[mc ∆ t + mL\]
= 0.01 × 4200 × 100 + 0.01 × 2.5 × 106
= 4200 + 25000 = 29200 J
∆W = P∆V
∆V \[= \text{mass}\left( \frac{1}{\text{final density}} - \frac{1}{\text{initial density}} \right)\]
\[∆ V = \left( \frac{0 . 01}{0 . 6} \right) - \left( \frac{0 . 01}{1000} \right) = 0 . 01699\]
∆W = P∆V = 0.01699 × 105 = 1699 J
Using the first law, we get
∆Q = ∆W + ∆U
∆U = ∆Q − ∆W = 29200 − 1699
= 27501 = 2.75 × 104 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

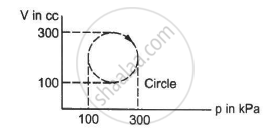
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
An adiabatic vessel of total volume V is divided into two equal parts by a conducting separator. The separator is fixed in this position. The part on the left contains one mole of an ideal gas (U = 1.5 nRT) and the part on the right contains two moles of the same gas. Initially, the pressure on each side is p. The system is left for sufficient time so that a steady state is reached. Find (a) the work done by the gas in the left part during the process, (b) the temperature on the two sides in the beginning, (c) the final common temperature reached by the gases, (d) the heat given to the gas in the right part and (e) the increase in the internal energy of the gas in the left part.
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
Define an isolated system.
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
"The mass and energy both are conserved in an isolated system", is the statement of ______.
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
Mathematical equation of first law of thermodynamics for isochoric process is ______.
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Define isochoric process
What is an isothermal process?
