Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
Solution
Usually, chemical reactions are carried out in open containers under constant atmospheric pressure. In such reactions, ∆V ≠ 0
∵ ∆U = Q - Pext ∆V ...(1)
Replacing Q by Qp and ∆U by Qp - Pext ∆V in equation (1) gives
Qp = ∆U + Pext ∆V
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
Find the change in the internal energy of 2 kg of water as it is heated from 0°C to 4°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and its densities at 0°C and 4°C are 999.9 kg m−3 and 1000 kg m−3 respectively. Atmospheric pressure = 105 Pa.
An adiabatic vessel of total volume V is divided into two equal parts by a conducting separator. The separator is fixed in this position. The part on the left contains one mole of an ideal gas (U = 1.5 nRT) and the part on the right contains two moles of the same gas. Initially, the pressure on each side is p. The system is left for sufficient time so that a steady state is reached. Find (a) the work done by the gas in the left part during the process, (b) the temperature on the two sides in the beginning, (c) the final common temperature reached by the gases, (d) the heat given to the gas in the right part and (e) the increase in the internal energy of the gas in the left part.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
"The mass and energy both are conserved in an isolated system", is the statement of ______.
The isothermal bulk modulus of a perfect gas at pressure P is numerically equal to ____________.
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
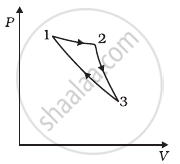
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
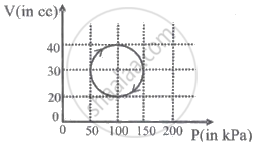
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
The V cc volume of gas having `γ = 5/2` is suddenly compressed to `(V/4)` cc. The initial pressure of the gas is p. The final pressure of the gas will be ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
Derive an expression for the work done during an isothermal process.
If the adiabatic ratio for a gas is 5/3, find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas at (i) constant volume (ii) constant pressure.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
What is an isothermal process?
