Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
उत्तर
The internal energy of a system is the sum of the potential and kinetic energy of all the system's constituents. In the preceding example, the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy is responsible for the significant increase in pressure and temperature of the hydrogen and oxygen mixture ignited by the spark.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
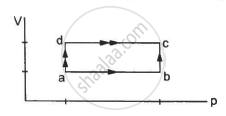
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
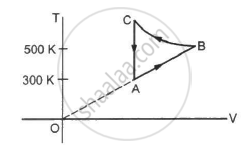
Consider the cyclic process ABCA, shown in figure, performed on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas. A total of 1200 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process. Find the work done by the gas during the part BC.
Find the change in the internal energy of 2 kg of water as it is heated from 0°C to 4°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and its densities at 0°C and 4°C are 999.9 kg m−3 and 1000 kg m−3 respectively. Atmospheric pressure = 105 Pa.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
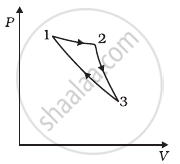
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
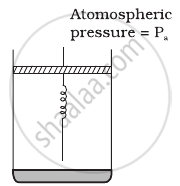
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
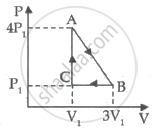
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
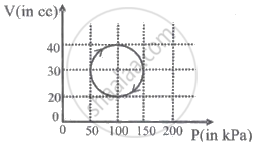
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
In an adiabatic process, ______.
If the adiabatic ratio for a gas is 5/3, find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas at (i) constant volume (ii) constant pressure.
What is true for an adiabatic process?
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Write a short note on isobar.
Define the isothermal process.
