Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
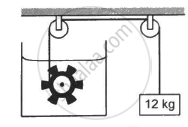
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
उत्तर
(a) Heat is not given to the liquid; instead, the mechanical work done is converted to heat. Also the container is adiabatic. So, no heat can enter or exit the system. This implies that the heat given to the liquid is zero.
(b) Since the 12 kg mass falls through a distance of 70 cm under gravity, energy is lost by this mass. As this mass is connected to the paddle wheel, energy lost by this mass is gained by the paddle wheel.
⇒">⇒ Work done on the liquid = PE lost by the 12 kg mass
Now,
PE lost by the 12 kg mass = mgh
= 12 × 10 × 0.70
= 84 J
(c) Suppose ∆t is the rise in temperature of the paddle wheel when the system gains energy.
⇒">⇒ 84 = ms∆t
If s is the specific heat of the system, then
84 = 1 × 4200 × ∆t .........(for 'm' = 1 kg)
\[∆ t = \frac{84}{4200} = \frac{1}{50} = 0 . 02 K\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
Heat energy is supplied at a constant rate to 100g of ice at 0 °C. The ice is converted into water at 0° C in 2 minutes. How much time will be required to raise the temperature of water from 0 °C to 20 °C? [Given: sp. heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1, sp. latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1].
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1K-1 whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1
(i) Which of the two is a good conductor of heat?
(ii) How is one led to the above conclusion?
(iii) If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
Name the S.I. unit of heat.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as heat reservoir ?
The S.I. unit of specific heat capacity is ______.
How much heat energy is released when 5.0 g of water at 20℃ changes into ice at 0℃? Take specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 K-1, Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1.
Name two green house gases ?
How will global warming disturb the ecological balance?
Without green house effect, the average temperature of earth’s surface would have been:
(a) – 18℃
(b) 33℃
(c) 0℃
(d) 15℃
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy.
The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both the objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat resistant box (meaning that the energy exchange takes place between the two objects only), then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box.
i. Heat is transferred from where to where?
ii. Which principle do we learn about from this process?
iii. How will you state the principle briefly?
iv. Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?
The specific heat capacity of a body depends on _____________ .
(i) State whether the specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same when its state changes from solid to liquid.
(ii) Give one example to support your answer.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as cooling.
The substances like water which have ........... Heat capacity warm up more slowly than substances like iron which have .......... heat capacity.
m kg of a substance of specific heat capacity s J/kg °C is heated so that its temperature rises from θ1°C to θ2°C. Write down the expression for the heat Q supplied.
Name the substance which has maximum specific heat capacity.
Explain, why does a wise farmer water his fields, if forecast is forst?
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1. Which of the two is a good conductor of heat? How is one led to this conclusion?
Why are athletes advised to put on extra clothes after competing on event?
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a thermal capacity of 966 J/°C. What is its specific heat capacity in S.I. units?
Solve the following problem.
What is the specific heat of metal if 50 cal of heat is needed to raise 6 kg of the metal from 20°C to 62 °C?
Calculate the ratio of two specific heats of polyatomic gas molecules.
The cold object the hot object enclosed in one box of heat-resistant material.
- What changes will occur in the two objects when temperature flows from those objects?
- Which principle can show that the energy exchange takes place between two objects only when kept in isolated system?
Consider the statement given below and choose the correct option.
Assertion: Radiation is a form of heat transfer which takes place only in vacuum.
Reason: The thermal energy is transferred from one part of a substance to another part without the actual movement of the atoms or molecules.
The heat capacity of the vessel of mass 100 kg is 8000 J/°K. Find its specific heat capacity.
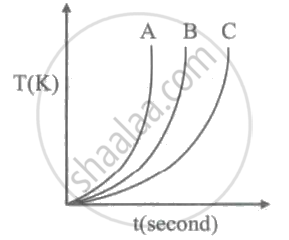
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
Two metals A and B have specific heat capacities in the ratio 2 : 3. If they are supplied the same amount of heat then
Which metal piece will show a greater rise in temperature given their masses is the same?
J/Kg °C is the unit of specific heat capacity.
Find the odd one out:
The difference between the two molar specific heats of gas is 9000 J/kg K. If the ratio of the two specific heats is 1.5, calculate the two molar specific heats.
The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume are denoted by Cp and Cv, respectively. If `gamma = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` and R is the universal gas constant, then Cv is equal to ______.
