Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
What is the specific heat of metal if 50 cal of heat is needed to raise 6 kg of the metal from 20°C to 62 °C?
उत्तर
Given: Q = 50 cal, m = 6 kg, ΔT = 62 - 20 = 42 °C.
To find: Specific heat (s)
Formula: Q = ms ΔT
Calculation: From formula,
s = `"Q"/("m" Delta"T") = 50/(6 xx 42) = 0.198` cal/kg °C
Specific heat of metal is copper 0.198 cal/kg °C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What property of water makes it an effective coolant?
A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20°C to ice at -10°C in 35 minutes. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in terms of watts.
Given: Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1°C-1
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1
Heat supplied to a solid change it into liquid. What is this change in the phase called?
The S.I. unit of specific heat capacity is ______.
Explain the term boiling ?
Give three reasons for the increase of green house gases.
How will rise in sea level affect population in coastal countries?
How will global warming disturb the ecological balance?
Without green house effect, the average temperature of earth’s surface would have been:
(a) – 18℃
(b) 33℃
(c) 0℃
(d) 15℃
Solve the following problems:
Equal heat is given to two objects A and B of mass 1 g. Temperature of A increases by 3°C and B by 5°C. Which object has more specific heat? And by what factor?
What is the specific heat capacity of boiling water?
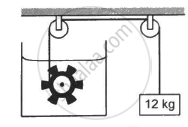
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
What change in heat energy occurs when lead at its melting point
solidifies without change in the temperature?
State the condition for the flow of heat energy from one body to another.
Does the specific heat capacity of a substance depend upon its mass and rise in temperature only?
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
A certain amount of heat Q will warm 1 g of material X by 3°C and 1 g of material Y by 4°C. Which material has a higher specific heat capacity?
An equal quantity of heat is supplied to two substances A and B. The substance A shows a greater rise in temperature. What can you say about the heat capacity of A as compared to that of B?
Some heat is provided to a body to raise its temperature by 25°C. What will be the corresponding rise in temperature of the body as shown on the Kelvin scale?
Why are athletes advised to put on extra clothes after competing on event?
A substance is in the form of a solid at 0°C. The amount of heat added to this substance and the temperature of the substance are plotted on the following graph:

If the specific heat capacity of the solid substance is 500 J/kg °G, find from the graph, the mass of the substance.
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
Numerical Problem.
How much heat energy is required to change 2 kg of ice at 0°C into water at 20°C? (Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 3,34,000 J/kg, Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 JKg–1K–1).
A monoatomic gas of pressure 'P' having volume 'V' expands isothermally to a volume '2V' and then adiabatically to a volume '16V'. The final pressure of the gas is ______.
(ratio of specific heats = `5/3`)
For a gas `"R"/"C"_"v" = 0.4,` where 'R' is the universal gas constant and 'Cv' is molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules which are ______.
To study energy exchange between hot and cold objects, the system of both objects is isolated from the environment by keeping them inside ______.
Match the columns:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| The SI unit of specific heat capacity | (a) Jkg−1°C−1 |
| (b) kg/m3 | |
| (c) calorie |
