Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
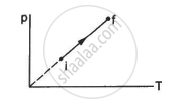
An ideal gas goes from the state i to the state f as shown in figure. The work done by the gas during the process ______________ .
विकल्प
is positive
is negative
is zero
cannot be obtained from this information
उत्तर
is zero
Work done by the gas during the process,
ΔW = P Δ V
Here,
P = Pressure
ΔV = change in volume
Since the process described in the figure is isochoric, P = kT. As volume remains constant (ΔV = 0), ΔW = 0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
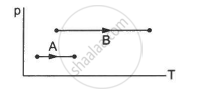
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
(a) Such a process is not possible.
(b) The work done by the system is positive.
(c) The temperature of the system must increase.
(d) Heat supplied to the gas is equal to the change in internal energy.
A 100 kg lock is started with a speed of 2.0 m s−1 on a long, rough belt kept fixed in a horizontal position. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the belt is 0.20. (a) Calculate the change in the internal energy of the block-belt system as the block comes to a stop on the belt. (b) Consider the situation from a frame of reference moving at 2.0 m s−1 along the initial velocity of the block. As seen from this frame, the block is gently put on a moving belt and in due time the block starts moving with the belt at 2.0 m s−1. calculate the increase in the kinetic energy of the block as it stops slipping past the belt. (c) Find the work done in this frame by the external force holding the belt.
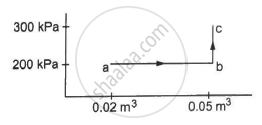
A substance is taken through the process abc as shown in figure. If the internal energy of the substance increases by 5000 J and a heat of 2625 cal is given to the system, calculate the value of J.
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
A cylinder containing one gram molecule of the gas was compressed adiabatically until its temperature rose from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the work done and heat produced in the gas (𝛾 = 1.5).
The internal energy of a system is ______
8 m3 of a gas is heated at the pressure 105 N/m2 until its volume increases by 10%. Then, the external work done by the gas is ____________.
Two samples A and B, of a gas at the same initial temperature and pressure are compressed from volume V to V/2; A isothermally and B adiabatically. The final pressure of A will be ______.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
