Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6 cm and 4 cm thick and weigh 1 kg and \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg each respectively. The shelf is 96 cm long and atmost can support a weight of 21 kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
उत्तर
Let x books of first type and y books of second type were accommodated.
Number of books cannot be negative.
Therefore, \[x, y \geq 0\]
| Thickness(cm) | Weight(kg) | |
| First type(x) | 6 | 1 |
| Second type(y) | 4 | 1.5 |
| Capacity of shelf | 96 | 21 |
Therefore, the constraints are
\[x + 1 . 5y \leq 21\]
Number of books = Z = \[x + y\] which is to be maximised
Thus, the mathematical formulation of the given linear programmimg problem is
MaxImize Z = \[x + y\]
subject to
\[6x + 4y \leq 96\]
\[x + 1 . 5y \leq 21\]
First we will convert inequations into equations as follows:
6x + 4y = 96, x + 1.5y = 21, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by 6x + 4y ≤ 96:
The line 6x + 4y = 96 meets the coordinate axes at A(16, 0) and \[B\left( 0, 24 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line
6x + 4y = 96. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the 6x + 4y = 96. So, the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation
6x + 4y ≤ 96.
Region represented by x + 1.5y ≤ 21:
The line x + 1.5y = 21 meets the coordinate axes at C(21, 0) and \[D\left( 0, 14 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + 1.5y = 21. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the inequation x + 1.5y ≤ 21. So,the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + 1.5y ≤ 21.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints 6x + 4y ≤ 96, x + 1.5y ≤ 21, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 are as follows.
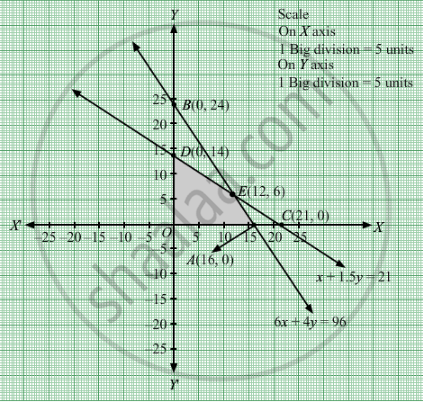 The corner points are O(0, 0), D(0, 14), E(12, 6), A(16, 0)
The corner points are O(0, 0), D(0, 14), E(12, 6), A(16, 0)
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows
| Corner point | Z= x + y |
| O | 0 |
| D | 14 |
| E | 18 |
| A | 16 |
The maximum value of Z is 18 which is attained at E \[\left( 12, 6 \right)\]
Thus, maximum number of books that can be arranged on shelf is 18 where 12 books are of first type and 6 books are the other type.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A dealer in rural area wishes to purchase a number of sewing machines. He has only Rs 5,760 to invest and has space for at most 20 items for storage. An electronic sewing machine cost him Rs 360 and a manually operated sewing machine Rs 240. He can sell an electronic sewing machine at a profit of Rs 22 and a manually operated sewing machine at a profit of Rs 18. Assuming that he can sell all the items that he can buy, how should he invest his money in order to maximize his profit? Make it as a LPP and solve it graphically.
Minimize :Z=6x+4y
Subject to : 3x+2y ≥12
x+y ≥5
0 ≤x ≤4
0 ≤ y ≤ 4
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B'. 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs Rs 10 per kg and 'B' cost Rs 8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids A and B of Mathematics for class XII. Each type of A requires 9 labour hours for fabricating and 1 labour hour for finishing. Each type of B requires 12 labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are 180 and 30, respectively. The company makes a profit of Rs 80 on each piece of type A and Rs 120 on each piece of type B. How many pieces of type A and type B should be manufactured per week to get maximum profit? Make it as an LPP and solve graphically. What is the maximum profit per week?
Solve the following L. P. P. graphically:Linear Programming
Minimize Z = 6x + 2y
Subject to
5x + 9y ≤ 90
x + y ≥ 4
y ≤ 8
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically Maximise Z = 4x + y
Subject to following constraints x + y ≤ 50
3x + y ≤ 90,
x ≥ 10
x, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 4y
Subject to
\[2x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 4y \leq 120\]
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to
\[x_1 + 3 x_2 \geq 3\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \geq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 2x + 3y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 1\]
\[10x + y \geq 5\]
\[x + 10y \geq 1\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
To maintain one's health, a person must fulfil certain minimum daily requirements for the following three nutrients: calcium, protein and calories. The diet consists of only items I and II whose prices and nutrient contents are shown below:
| Food I | Food II | Minimum daily requirement | |
| Calcium Protein Calories |
10 5 2 |
4 6 6 |
20 20 12 |
| Price | Rs 0.60 per unit | Rs 1.00 per unit |
Find the combination of food items so that the cost may be minimum.
One kind of cake requires 200 g of flour and 25 g of fat, and another kind of cake requires 100 g of flour and 50 g of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 5 kg of flour and 1 kg of fat assuming that there is no storage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
A factory manufactures two types of screws, A and B, each type requiring the use of two machines - an automatic and a hand-operated. It takes 4 minute on the automatic and 6 minutes on the hand-operated machines to manufacture a package of screws 'A', while it takes 6 minutes on the automatic and 3 minutes on the hand-operated machine to manufacture a package of screws 'B'. Each machine is available for at most 4 hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a package of screws 'A' at a profit of 70 P and screws 'B' at a profit of Rs 1. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he can manufacture, how many packages of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximize his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
A company produces two types of goods, A and B, that require gold and silver. Each unit of type A requires 3 gm of silver and 1 gm of gold while that of type B requires 1 gm of silver and 2 gm of gold. The company can produce 9 gm of silver and 8 gm of gold. If each unit of type A brings a profit of Rs 40 and that of type B Rs 50, find the number of units of each type that the company should produce to maximize the profit. What is the maximum profit?
A publisher sells a hard cover edition of a text book for Rs 72.00 and paperback edition of the same ext for Rs 40.00. Costs to the publisher are Rs 56.00 and Rs 28.00 per book respectively in addition to weekly costs of Rs 9600.00. Both types require 5 minutes of printing time, although hardcover requires 10 minutes binding time and the paperback requires only 2 minutes. Both the printing and binding operations have 4,800 minutes available each week. How many of each type of book should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A firm manufactures headache pills in two sizes A and B. Size A contains 2 grains of aspirin, 5 grains of bicarbonate and 1 grain of codeine; size B contains 1 grain of aspirin, 8 grains of bicarbonate and 66 grains of codeine. It has been found by users that it requires at least 12 grains of aspirin, 7.4 grains of bicarbonate and 24 grains of codeine for providing immediate effects. Determine graphically the least number of pills a patient should have to get immediate relief. Determine also the quantity of codeine consumed by patient.
A manufacturer produces two types of steel trunks. He has two machines A and B. For completing, the first types of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 3 hours on machine B, whereas the second type of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 2 hours on machine B. Machines A and B can work at most for 18 hours and 15 hours per day respectively. He earns a profit of Rs 30 and Rs 25 per trunk of the first type and the second type respectively. How many trunks of each type must he make each day to make maximum profit?
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 200 passengers. A profit of Rs 400 is made on each first class ticket and a profit of Rs 600 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves at least 20 seats of first class. However, at least 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class to the first class. Determine how many each type of tickets must be sold in order to maximize the profit for the airline. What is the maximum profit.
A cottage industry manufactures pedestal lamps and wooden shades, each requiring the use of grinding/cutting machine and sprayer. It takes 2 hours on the grinding/cutting machine and 3 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a pedestal lamp while it takes 1 hour on the grinding/cutting machine and 2 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a shade. On any day, the sprayer is available for at most 20 hours and the grinding/cutting machine for at most 12 hours. The profit from the sale of a lamp is ₹5.00 and a shade is ₹3.00. Assuming that the manufacturer sell all the lamps and shades that he produces, how should he schedule his daily production in order to maximise his profit?
A producer has 30 and 17 units of labour and capital respectively which he can use to produce two type of goods x and y. To produce one unit of x, 2 units of labour and 3 units of capital are required. Similarly, 3 units of labour and 1 unit of capital is required to produce one unit of y. If x and y are priced at Rs 100 and Rs 120 per unit respectively, how should be producer use his resources to maximize the total revenue? Solve the problem graphically.
A firm makes items A and B and the total number of items it can make in a day is 24. It takes one hour to make an item of A and half an hour to make an item of B. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. The profit on an item of A is Rs 300 and on one item of B is Rs 160. How many items of each type should be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
A company sells two different products, A and B. The two products are produced in a common production process, which has a total capacity of 500 man-hours. It takes 5 hours to produce a unit of A and 3 hours to produce a unit of B. The market has been surveyed and company officials feel that the maximum number of unit of A that can be sold is 70 and that for B is 125. If the profit is Rs 20 per unit for the product A and Rs 15 per unit for the product B, how many units of each product should be sold to maximize profit?
A manufacturer makes two products, A and B. Product A sells at Rs 200 each and takes 1/2 hour to make. Product B sells at Rs 300 each and takes 1 hour to make. There is a permanent order for 14 units of product A and 16 units of product B. A working week consists of 40 hours of production and the weekly turn over must not be less than Rs 10000. If the profit on each of product A is Rs 20 and an product B is Rs 30, then how many of each should be produced so that the profit is maximum? Also find the maximum profit.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend ₹2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to ₹5 per km. He has ₹100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
There are two factories located one at place P and the other at place Q. From these locations, a certain commodity is to be delivered to each of the three depots situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the depots are respectively 5, 5 and 4 units of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories at P and Q are respectively 8 and 6 units. The cost of transportation per unit is given below:
| From \ To | Cost (in ₹) | ||
| A | B | C | |
| P | 160 | 100 | 150 |
| Q | 100 | 120 | 100 |
How many units should be transported from each factory to each depot in order that the transportation cost is minimum. What will be the minimum transportation cost?
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
A manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes two models A and B of an article. The making of one item of model A requires 2 hours of work by a skilled man and 2 hours work by a semi-skilled man. One item of model B requires 1 hour by a skilled man and 3 hours by a semi-skilled man. No man is expected to work more than 8 hours per day. The manufacturer's profit on an item of model A is ₹ 15 and on an item of model B is ₹ 10. How many items of each model should be made per day in order to maximize daily profit? Formulate the above LPP and solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
The graph of the inequality 3X − 4Y ≤ 12, X ≤ 1, X ≥ 0, Y ≥ 0 lies in fully in
Find the feasible solution of linear inequation 2x + 3y ≤ 12, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 by graphically
The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem: Max P = 2x + 3y subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 2y ≤ 9, 2x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 8, is ______
The maximum of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then the objective function Z has both a maximum and a minimum value on R and ____________.
Minimise z = – 3x + 4y subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 What will be the minimum value of z ?
The constraints –x1 + x2 ≤ 1, –x1 + 3x2 ≤ 9, x1x2 ≥ 0 define on ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = 3x + 3.5y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 240,
3x + 1.5y ≥ 270,
1.5x + 2y ≤ 310,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
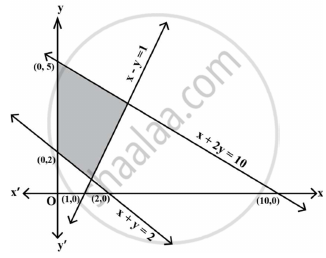
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
If x – y ≥ 8, x ≥ 3, y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 then find the coordinates of the corner points of the feasible region.
