Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A long straight wire of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across its area of cross-section. The ratio of the magnitude of magnetic field `vecB_1` at `a/2` and `vecB_2` at distance 2a is ______.
विकल्प
`1/2`
1
2
4
उत्तर
A long straight wire of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across its area of cross-section. The ratio of the magnitude of magnetic field `vecB_1` at `a/2` and `vecB_2` at distance 2a is 1.
Explanation:
Consider two amperian loops of radius `a/2` and 2a. Applying Ampere's circuital law for these loops.
We get `ointB.dL = μ_0I_{"enclosed"}`
For the smaller loop,
`B_1 xx 2pi a/2 = mu_0 xx pia^2 1 xx (a/2)^2`
`mu_0I xx 1/4 = (mu_0I)/4`
`B_1 = (mu_0I)/(4pia)`
`B_2 xx 2pi(2a) = mu_0I`
`B_2 = (mu_0I)/(4pia)`
∴ B1/B2 = `(mu_0I)/(4pia) xx (4pia)/(mu_0I) = 1`
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
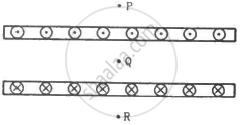
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
What is magnetic permeability?
State Ampere’s circuital law.
A solenoid of length 0.6 m has a radius of 2 cm and is made up of 600 turns If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is:
Ampere's circuital law is used to find out ______
