Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A long straight wire of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across its area of cross-section. The ratio of the magnitude of magnetic field `vecB_1` at `a/2` and `vecB_2` at distance 2a is ______.
पर्याय
`1/2`
1
2
4
उत्तर
A long straight wire of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across its area of cross-section. The ratio of the magnitude of magnetic field `vecB_1` at `a/2` and `vecB_2` at distance 2a is 1.
Explanation:
Consider two amperian loops of radius `a/2` and 2a. Applying Ampere's circuital law for these loops.
We get `ointB.dL = μ_0I_{"enclosed"}`
For the smaller loop,
`B_1 xx 2pi a/2 = mu_0 xx pia^2 1 xx (a/2)^2`
`mu_0I xx 1/4 = (mu_0I)/4`
`B_1 = (mu_0I)/(4pia)`
`B_2 xx 2pi(2a) = mu_0I`
`B_2 = (mu_0I)/(4pia)`
∴ B1/B2 = `(mu_0I)/(4pia) xx (4pia)/(mu_0I) = 1`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write Maxwell's generalization of Ampere's circuital law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is `I=varepsilon_0 (dphi_E)/dt,`where ΦE is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
In order to have a current in a long wire, it should be connected to a battery or some such device. Can we obtain the magnetic due to a straight, long wire by using Ampere's law without mentioning this other part of the circuit?
In a coaxial, straight cable, the central conductor and the outer conductor carry equal currents in opposite directions. The magnetic field is zero
(a) outside the cable
(b) inside the inner conductor
(c) inside the outer conductor
(d) in between the tow conductors.
Ampere’s circuital law is given by _______.
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C ______.
- `oint B.dl = +- 2μ_0I`
- the value of `oint B.dl` is independent of sense of C.
- there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular.
- B vanishes everywhere on C.
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
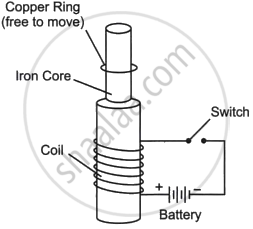
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
