Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
उत्तर
1. The phenomenon is called self-induction.
2. ΔI = (5 – 0) A = 5 A, Δt = 20 × 10-3 sec.
`e = L (ΔI)/(Δt)`
`L = e × (Δt)/(ΔI)`
= `(500 xx 20 xx 10^(-3))/5 "H"`
= 2H
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write Maxwell's generalization of Ampere's circuital law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is `I=varepsilon_0 (dphi_E)/dt,`where ΦE is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Electron drift speed is estimated to be of the order of mm s−1. Yet large current of the order of few amperes can be set up in the wire. Explain briefly.
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
A thin but long, hollow, cylindrical tube of radius r carries i along its length. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r/2 from the surface (a) inside the tube (b) outside the tube.
A solid wire of radius 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnetic field B at a point at a distance (a) 2 cm (b) 10 cm and (c) 20 cm away from the axis. Sketch a graph B versus x for 0 < x < 20 cm.
Define ampere.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
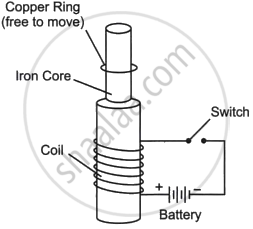
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
