Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thin but long, hollow, cylindrical tube of radius r carries i along its length. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r/2 from the surface (a) inside the tube (b) outside the tube.
उत्तर
(a) The magnetic field inside any conducting tube is always zero.
∴ Magnetic field inside the tube at a distance r/2 from the surface = 0
(b) Let the point outside the tube with distance \[\frac{r}{2}\] be P.
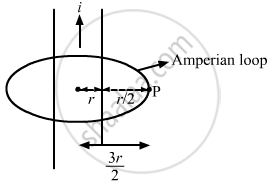
∴ Net distance from centre, r' = \[r + \frac{r}{2} = \frac{3r}{2}\]
Length of the loop, l = \[2\pi \times \frac{3}{2}r = 3\pi r\]
On applying Ampere's law, we get
\[ \Rightarrow B \times 3\pi r = \mu_0 i\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{3\pi r}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
State Ampere’s circuital law.
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
Explain Ampere’s circuital law.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
A long straight wire of a circular cross-section of radius ‘a’ carries a steady current ‘I’. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section. Apply Ampere’s circuital law to calculate the magnetic field at a point ‘r’ in the region for (i) r < a and (ii) r > a.
In order to have a current in a long wire, it should be connected to a battery or some such device. Can we obtain the magnetic due to a straight, long wire by using Ampere's law without mentioning this other part of the circuit?
A solid wire of radius 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnetic field B at a point at a distance (a) 2 cm (b) 10 cm and (c) 20 cm away from the axis. Sketch a graph B versus x for 0 < x < 20 cm.
What is magnetic permeability?
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Calculate the magnetic field inside and outside of the long solenoid using Ampere’s circuital law
A straight wire of diameter 0.5 mm carrying a current of 1 A is replaced by another wire of 1 mm diameter carrying the same current. The strength of the magnetic field far away is ______.
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, then which statement is correct?
The force required to double the length of a steel wire of area 1 cm2, if it's Young's modulus Y = `2 xx 10^11/m^2` is:
A solenoid of length 0.6 m has a radius of 2 cm and is made up of 600 turns If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is:
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C ______.
- `oint B.dl = +- 2μ_0I`
- the value of `oint B.dl` is independent of sense of C.
- there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular.
- B vanishes everywhere on C.
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
