Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C ______.
- `oint B.dl = +- 2μ_0I`
- the value of `oint B.dl` is independent of sense of C.
- there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular.
- B vanishes everywhere on C.
पर्याय
a and b
a and c
b and c
c and d
उत्तर
b and c
Explanation:
Ampere’s law gives another method to calculate the magnetic field due to a given current distribution.
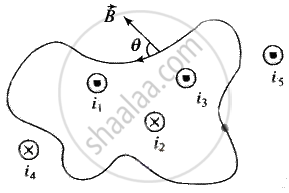
Line integral of the magnetic field `vecB` around any closed curve is equal to μ0 times the net current i threading through the area enclosed by the curve, i.e.
`oint vecB * vec(dl) = mu_0 sumi = mu_0 (i_1 + i_3 - i_2)`
Total current crossing the above area is `(i_1 + i_3 - i_2)`. Any current outside the area is not included in net current. (Outward ⊙ → + ve, Inward ⊗ → – ve)
Applying the Ampere's circuital law, we have
`ointB* dl = i_0 (I - I) = 0` (because current is in opposite sense)
Also, there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular and hence, `oint_c B*dl = 0`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Electron drift speed is estimated to be of the order of mm s−1. Yet large current of the order of few amperes can be set up in the wire. Explain briefly.
Obtain an expression for magnetic induction along the axis of the toroid.
Explain Ampere’s circuital law.
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
A long, cylindrical tube of inner and outer radii a and b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnitude filed at a point (a) just inside the tube (b) just outside the tube.
A solid wire of radius 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnetic field B at a point at a distance (a) 2 cm (b) 10 cm and (c) 20 cm away from the axis. Sketch a graph B versus x for 0 < x < 20 cm.
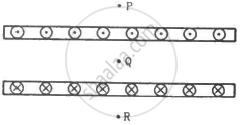
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
A solenoid of length 0.6 m has a radius of 2 cm and is made up of 600 turns If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is:
A thick current carrying cable of radius ‘R’ carries current ‘I’ uniformly distributed across its cross-section. The variation of magnetic field B(r) due to the cable with the distance ‘r’ from the axis of the cable is represented by:
