Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point charge is brought inside an electric field. The electric field at a nearby point
(a) will increase if the charge is positive
(b) will decrease if the charge is negative
(c) may increase if the charge is positive
(d) may decrease if the charge is negative
उत्तर
(c) may increase if the charge is positive
(d) may decrease if the charge is negative
Electric field is a vector quantity. The electric field at a point due to a number of point charges is the vector sum of electric field due to individual charges. So, when a positive charge is brought into an electric field, the electric field due to the positive charge is added to the electric field already present. Therefore, the electric field increases.
When a negative charge is brought into an electric field, the electric field due to the negative charge is subtracted from the electric field already present. Therefore, the electric field decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A proton and an electron are placed in a uniform electric field.
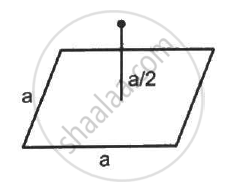
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
The electric force experienced by a charge of 1.0 × 10−6 C is 1.5 × 10−3 N. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the position of the charge.
A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its length. It is bent in the shape of a semicircle. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the centre of curvature of the semicircle.
A positive charge q is placed in front of a conducting solid cube at a distance d from its centre. Find the electric field at the centre of the cube to the charges appearing on its surface.
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
Electric charges are of ______.
Conductors are materials that allow ______.
Assertion: The positive charge particle is placed in front of a spherical uncharged conductor. The number of lines of forces terminating on the sphere will be more than those emerging from it.
Reason: The surface charge density at a point on the sphere nearest to the point charge will be negative and maximum in magnitude compared to other points on the sphere.
Electric field lines provide information about ______.
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and the force acting between them is F. If a medium of dielectric constant 4 is introduced around them, the force now will be ______.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field E due to a hollow spherical conductor of radius R as a function of distance from the centre of the sphere?
A particle of mass m and charge q is placed at rest in a uniform electric field E and then released. The kinetic energy gained by the particle after moving a distance of y will be ______.
The potential at a point x (measured in µm) due to some charges situated on the X-axis is given by v(x) = `20/((x^2 - 4)` V. The electric field E at x = 4 µm is given by ______.
