Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A quadrilateral field of unequal has a longer diagonal with 140m. The perpendiculars from opposite vertives upon this diagonal are 20m and 14m. Find the area of the field.
उत्तर
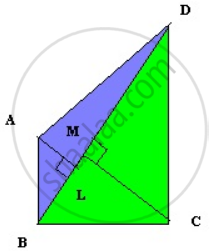
In quadrilateral ABCD, the sides AB, BC, CD and AD are unequal.
The longer diagonal BD = 140m
AM ⊥ BD, CL ⊥ BD
AM = 20m and CL = 14m.
We split a quadrilateral into triangles and find its area.
We know that,
Area of a Triangle = `(1)/(2)"b.h" "i.e" (1)/(2)("Base" xx "Height")`
Ar(ΔABD) = `(1)/(2)"BD" xx "AL";(Δ"CBD") = (1)/(2)"BD" xx "CM"`
Ar(QuadABCD) = Ar(ΔABD) + Ar(ΔCBD)
= `(1)/(2)"BD" xx "AL" + (1)/(2)"BD" xx "CM"`
= `(1)/(2)"BD" xx ("AL" + "CM")`
= `(1)/(2) xx 140 xx (20 + 14)`
= 70 x 34
= 2380m2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular plot 85 m long and 60 m broad is to be covered with grass leaving 5 m all around. Find the area to be laid with grass.
How many tiles, each of area 400 cm2, will be needed to pave a footpath which is 2 m wide and surrounds a grass plot 25 m long and 13 m wide?
Calculate the area of the figure given below: which is not drawn scale.
The figure given below shows the cross-section of a concrete structure. Calculate the area of cross-section if AB = 1.8 cm, CD = 0.6 m, DE = 0.8 m, EF = 0.3 m and AF = 1.2 m.
A floor that measures 15 m x 8 m is to be laid with tiles measuring 50 cm x 25 cm. Find the number of tiles required.
Further, if a carpet is laid on the floor so that a space of 1 m exists between its edges and the edges of the floor, what fraction of the floor is left uncovered?
A triangle and a parallelogram have the same base and the same area. If the side of the triangle is 26 cm, 28 cm, and 30 cm and the parallelogram stands on the base 28 cm, find the height of the parallelogram.
Vertices of given triangles are taken in order and their areas are provided aside. Find the value of ‘p’.
| Vertices | Area (sq.units) |
| (0, 0), (p, 8), (6, 2) | 20 |
Vertices of given triangles are taken in order and their areas are provided aside. Find the value of ‘p’.
| Vertices | Area (sq.units) |
| (p, p), (5, 6), (5, –2) | 32 |
Find the area of quadrilateral BCEG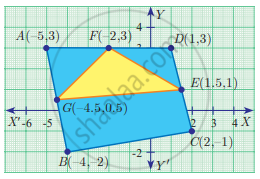
PQRS is a rectangle formed by joining the points P(– 1, – 1), Q(– 1, 4), R(5, 4) and S(5, – 1). A, B, C and D are the mid-points of PQ, QR, RS and SP respectively. Is the quadrilateral ABCD a square, a rectangle or a rhombus? Justify your answer.
