Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
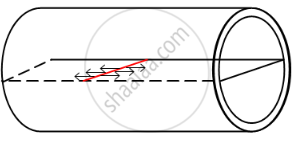
A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
उत्तर
As the angle of contact is 0, there is no force between the surface of the tube and the liquid. The diameter of the liquid surface is pulled on both sides by equal and opposite forces of surface tension. This results in no net force remaining on the surface of the liquid. Hence, the liquid stays in equilibrium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The surface tension of water at 0ºc is 75·5 dyne/cm. Find surface tension of water at 25°C. [ α for water = 0·0021/°C ]
The total free surface energy of a liquid drop is `pisqrt2` times the surface tension of the liquid. Calculate the diameter of the drop in S.l. unit.
When the size of a soap bubble is increased by pushing more air in it, the surface area increases. Does it mean that the average separation between the surface molecules is increased?
If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of semicircular cross section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and on the flat part are in ratio
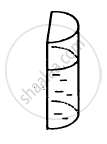
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water. The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points. If the density of the metal is 8000 kg/m3, find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece.

A solid sphere of radius 5 cm floats in water. If a maximum load of 0.1 kg can be put on it without wetting the load, find the specific gravity of the material of the sphere.
Describe an experiment to prove that friction depends on the nature of a surface.
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
A water drop of radius R' splits into 'n' smaller drops, each of radius 'r'. The work done in the process is ______.
T = surface tension of water
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
The wear and tear in the machine part is due to ______.
The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a ms–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?
A drop of water and a soap bubble have the same radii. Surface tension of soap solution is half of that of water. The ratio of excess pressure inside the drop and bubble is ______.
Define angle of contact.
