Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
विकल्प
when the mass is at the highest point
when the mass is at the lowest point
when the wire is horizontal
at an angle of cos−1(1/3) from the upward vertical.
उत्तर
If the velocity of the mass is a maximum at the bottom, then the string experiences tension due to both the weight of the mass and the high centrifugal force. Both these factors weigh the mass downwards. The tension is therefore, maximum at the lowest point, causing the string to most likely break at the bottom.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for excess pressure inside a drop of liquid.
Water rises to a height 3.2 cm in a glass capillary tube. Find the height to which the same water will rise in another glass capillary having half area of cross section.
Explain why A drop of liquid under no external forces is always spherical in shape
Two narrow bores of diameters 3.0 mm and 6.0 mm are joined together to form a U-tube open at both ends. If the U-tube contains water, what is the difference in its levels in the two limbs of the tube? Surface tension of water at the temperature of the experiment is 7.3 × 10–2 N m–1. Take the angle of contact to be zero and density of water to be 1.0 × 103 kg m–3 (g = 9.8 m s–2)
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
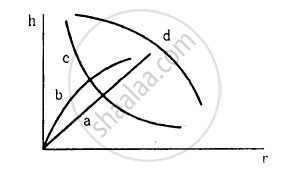
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water. The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points. If the density of the metal is 8000 kg/m3, find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece.

A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. Water can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9.
A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in K.oil (in the following figure). Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in K.oil. Specific gravity of K.oil is 0.8 and that of ice is 0.9.

Explain the capillary action.
Derive an expression for capillary rise for a liquid having a concave meniscus.
The water droplets are spherical in free fall due to ______
A capillary of diameter d mm is dipped in water such that the water rises to a height of 30 mm. If the radius of the capillary is made `(2/3)` of its previous value, then compute the height up to which water will rise in the new capillary?
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
For a surface molecule ______.
- the net force on it is zero.
- there is a net downward force.
- the potential energy is less than that of a molecule inside.
- the potential energy is more than that of a molecule inside.
