Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
उत्तर
Given:
Depth of the stone from the water surface, h = 500 m
Area of the plane surface of the large stone, A = 2 m2
Density of water, ρw = 103 kgm−3
Force (F) is given by
\[F = P \times A = \left( h \rho_w \times g \right)A \left( P = \text{ Pressure }\right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{ F }= \left( 500 \times {10}^3 \times 10 \right) \times 2\]
\[ = {10}^7 \text{ N/ m}^2\]
The force does not depend on the orientation of the rock when the surface area of the stone remains the same.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A U-shaped wire is dipped in a soap solution and removed. The thin soap film formed between the wire and the light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (which includes the small weight of the slider). The length of the slider is 30 cm. What is the surface tension of the film?
The total free surface energy of a liquid drop is `pisqrt2` times the surface tension of the liquid. Calculate the diameter of the drop in S.l. unit.
The contact angle between pure water and pure silver is 90°. If a capillary tube made of silver is dipped at one end in pure water, will the water rise in the capillary?
If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
Consider a small surface area of 1 mm2 at the top of a mercury drop of radius 4.0 mm. Find the force exerted on this area (a) by the air above it (b) by the mercury below it and (c) by the mercury surface in contact with it. Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Neglect the effect of gravity. Assume all numbers to be exact.
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
The property of _______ of a liquid surface enables the water droplets to move upward in plants.
How does surface tension help a plant?
What are the factors affecting the surface tension of a liquid?
What is surface tension? Explain the applications of surface tension.
For a surface molecule ______.
- the net force on it is zero.
- there is a net downward force.
- the potential energy is less than that of a molecule inside.
- the potential energy is more than that of a molecule inside.
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
We have three identical perfectly black plates. The temperatures of first and third plate is T and 3T. What is the temperature of second plate if system is in equilibrium?
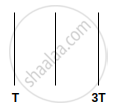
Two blocks of masses m and M are connected by means of a metal wire of cross-sectional area A passing over a frictionless fixed pully as shown in the figure. The system is then released. If M = 2m, then the stress produced in the wire is ______.