Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the capillary action.
उत्तर
If one end of a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid which partially or completely wets the surface of the capillary, the level of liquid in the capillary rises. On the other hand, if the capillary tube is dipped in a liquid which does not wet its surface, the level of liquid in the capillary drops. The phenomenon of the rise or fall of a liquid inside a capillary tube when it is dipped in the liquid is called capillarity.
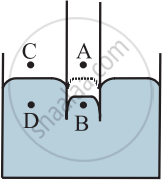

Consider the points A, B, C, and D such that
i) Point A is just above the convex surface and inside the capillary.
ii) Point B is just below the convex surface inside the capillary.
iii) Point C is just above the plane surface outside the capillary.
iv) Point D is just below the plane surface and outside the capillary, and below the point C.
Let PA, PB, PC, and PD be the pressure values at points A, B, C, and D, respectively. The pressure on the concave side is always greater than that on the convex side.
Capillary fall:
Consider a capillary tube dipped in a liquid which does not wet the surface. The shape of the liquid meniscus in the capillary is upper convex.
∴ PB > PA
As points A and C are at the same level, the pressure at both these points is the same, and it is the atmospheric pressure.
∴ PA = PC
Between the points C and D, the surface is plane.
∴ PC = PD = PA
∴ PB > PD.
But the points B and D are at the same horizontal level. Thus, in order to maintain the same pressure, the liquid in the capillary rushes out of the capillary. Because of this, there is a drop in the level of liquid inside the capillary, as shown.
Capillary rise:
Consider a capillary tube dipped in a liquid which wets the surface. The shape of the liquid meniscus in the capillary is concave.
∴ PA > PB
As points A and C are at the same level, the pressure at both these points is the same, and it is the atmospheric pressure.
∴ PA = PC
Between the points C and D, the surface is plane.
∴ PC = PD = PA
∴ PD > PB.
But the points B and D are at the same horizontal level. Thus, in order to maintain the same pressure, the liquid in the capillary rushes into the capillary. Because of this, there is a rise in the level of liquid outside the capillary, as shown.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The energy of the free surface of a liquid drop is 5π times the surface tension of the liquid. Find the diameter of the drop in C.G.S. system.
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
Explain why The angle of contact of mercury with glass is obtuse, while that of water with glass is acute
Explain why Surface tension of a liquid is independent of the area of the surface
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Surface tension of liquids generally . . . with temperatures (increases / decreases)
Define surface tension and surface energy.
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
When a glass capillary tube is dipped at one end in water, water rises in the tube. The gravitational potential energy is thus increased. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
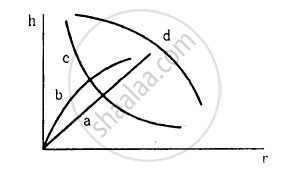
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
(a) the material
(b) the length
(c) the outer radius
(d) the inner radius of the tube
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
(a) the material of the solid
(b) the material of the liquid
(c) the shape of the solid
(d) the mass of the solid
Two large glass plates are placed vertically and parallel to each other inside a tank of water with separation between the plates equal to 1 mm. Find the rise of water in the space between the plates. Surface tension of water = 0.075 Nm−1.
Consider an ice cube of edge 1.0 cm kept in a gravity-free hall. Find the surface area of the water when the ice melts. Neglect the difference in densities of ice and water.
A wire forming a loop is dipped into soap solution and taken out so that a film of soap solution is formed. A loop of 6.28 cm long thread is gently put on the film and the film is pricked with a needle inside the loop. The thread loop takes the shape of a circle. Find the tension the the thread. Surface tension of soap solution = 0.030 N m−1.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. Water can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9.
A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in K.oil (in the following figure). Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in K.oil. Specific gravity of K.oil is 0.8 and that of ice is 0.9.

Solve the previous problem if the lead piece is fastened on the top surface of the block and the block is to float with its upper surface just dipping into water.
A solid sphere of radius 5 cm floats in water. If a maximum load of 0.1 kg can be put on it without wetting the load, find the specific gravity of the material of the sphere.
Water level is maintained in a cylindrical vessel up to a fixed height H. The vessel is kept on a horizontal plane. At what height above the bottom should a hole be made in the vessel so that the water stream coming out of the hole strikes the horizontal plane at the greatest distance from the vessel.
Derive an expression for capillary rise for a liquid having a concave meniscus.
Explain the phenomena of surface tension on the basis of molecular theory.
How does surface tension help a plant?
Describe an experiment to prove that friction depends on the nature of a surface.
Define the surface tension of a liquid.
What do you mean by capillarity or capillary action?
What is capillarity?
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
A capillary of diameter d mm is dipped in water such that the water rises to a height of 30 mm. If the radius of the capillary is made `(2/3)` of its previous value, then compute the height up to which water will rise in the new capillary?
Water rises in a capillary tube of radius r upto a height h. The mass of water in a capillary is m. The mass of water that will rise in a capillary of radius `"r"/4` will be ______.
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
The excess of pressure, due to surface tension, on a spherical liquid drop of radius 'R' is proportional to ______.
The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of the water column and 'h' is the height of water in the capillary. The inner circumference of the capillary is ______.
(surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
The length of a needle floating on water is 2 cm. The additional force due to surface tension required to pull the needle out of water will be (S.T. of water = 7.0 × 10−2 N/m).
The angle of contact at the interface of water-glass is 0°, Ethylalcohol-glass is 0°, Mercury-glass is 140° and Methyliodide-glass is 30°. A glass capillary is put in a trough containing one of these four liquids. It is observed that the meniscus is convex. The liquid in the trough is ______.
Is surface tension a vector?
Eight droplets of water each of radius 0.2 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the decrease in the surface area.
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
A drop of water and a soap bubble have the same radii. Surface tension of soap solution is half of that of water. The ratio of excess pressure inside the drop and bubble is ______.
The excess pressure inside a liquid drop is 500 Nm-2. If the radius of the drop is 2 mm, the surface tension of the liquid is x × 10-3 Nm-1. The value of x is ______.
When one end of the capillary is dipped in water, the height of water column is 'h'. The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of water column. The inner circumference of capillary is ______.
(Surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
A liquid drop of density ρ is floating half immersed in a liquid of density d. The diameter of the liquid drop is ______.
(ρ > d, g = acceleration due to gravity, T = surface tension)
Work done to blow a bubble of volume V is W. The work done in blowing a bubble of volume 2V will be ______.
In most liquids, with the rise in temperature, the surface tension of a liquid ______.
A spherical liquid drop of radius R is divided into eight equal droplets. If surface tension is T, then the work done in this process will be ______.
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
Calculate (i) the pressure due to the weight of the water at a depth of 2.5 m and (ii) the depth below the surface of water at which the pressure due to the weight of the water equals 1.0 atm.
