Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the capillary action.
Solution
If one end of a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid which partially or completely wets the surface of the capillary, the level of liquid in the capillary rises. On the other hand, if the capillary tube is dipped in a liquid which does not wet its surface, the level of liquid in the capillary drops. The phenomenon of the rise or fall of a liquid inside a capillary tube when it is dipped in the liquid is called capillarity.
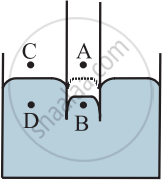

Consider the points A, B, C, and D such that
i) Point A is just above the convex surface and inside the capillary.
ii) Point B is just below the convex surface inside the capillary.
iii) Point C is just above the plane surface outside the capillary.
iv) Point D is just below the plane surface and outside the capillary, and below the point C.
Let PA, PB, PC, and PD be the pressure values at points A, B, C, and D, respectively. The pressure on the concave side is always greater than that on the convex side.
Capillary fall:
Consider a capillary tube dipped in a liquid which does not wet the surface. The shape of the liquid meniscus in the capillary is upper convex.
∴ PB > PA
As points A and C are at the same level, the pressure at both these points is the same, and it is the atmospheric pressure.
∴ PA = PC
Between the points C and D, the surface is plane.
∴ PC = PD = PA
∴ PB > PD.
But the points B and D are at the same horizontal level. Thus, in order to maintain the same pressure, the liquid in the capillary rushes out of the capillary. Because of this, there is a drop in the level of liquid inside the capillary, as shown.
Capillary rise:
Consider a capillary tube dipped in a liquid which wets the surface. The shape of the liquid meniscus in the capillary is concave.
∴ PA > PB
As points A and C are at the same level, the pressure at both these points is the same, and it is the atmospheric pressure.
∴ PA = PC
Between the points C and D, the surface is plane.
∴ PC = PD = PA
∴ PD > PB.
But the points B and D are at the same horizontal level. Thus, in order to maintain the same pressure, the liquid in the capillary rushes into the capillary. Because of this, there is a rise in the level of liquid outside the capillary, as shown.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The surface tension of water at 0°C is 75.5 dyne/cm. Calculate surface tension of water at 25°C.
(α for water = 2.7×10-3/°C)
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
Explain why Water on a clean glass surface tends to spread out while mercury on the same surface tends to form drops. (Put differently, water wets glass while mercury does not.)
Explain why A drop of liquid under no external forces is always spherical in shape
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Surface tension of liquids generally . . . with temperatures (increases / decreases)
Define surface tension and surface energy.
Calculate the work done in increasing the radius of a soap bubble in air from 1 cm to 2 cm. The surface tension of soap solution is 30 dyne/cm. (Π = 3.142).
A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
If a mosquito is dipped into water and released, it is not able to fly till it is dry again. Explain
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
(a) the material of the solid
(b) the material of the liquid
(c) the shape of the solid
(d) the mass of the solid
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
Consider an ice cube of edge 1.0 cm kept in a gravity-free hall. Find the surface area of the water when the ice melts. Neglect the difference in densities of ice and water.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water. The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points. If the density of the metal is 8000 kg/m3, find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece.

A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
Solve the previous problem if the lead piece is fastened on the top surface of the block and the block is to float with its upper surface just dipping into water.
Twenty-seven droplets of water, each of radius 0.1 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the change in surface energy. Surface tension of water is 0.072 N/m.
A drop of mercury of radius 0.2 cm is broken into 8 droplets of the same size. Find the work done if the surface tension of mercury is 435.5 dyn/cm.
Insect moves over the surface of water because of ______.
Define surface tension
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
The property of _______ of a liquid surface enables the water droplets to move upward in plants.
A certain number of spherical drops of a liquid of radius R coalesce to form a single drop of radius R and volume V. If T is the surface tension of the liquid, then
The wettability of a surface by a liquid depends primarily on
Define the surface tension of a liquid.
Distinguish between cohesive and adhesive forces.
What do you mean by capillarity or capillary action?
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
A spherical soap bubble A of radius 2 cm is formed inside another bubble B of radius 4 cm. Show that the radius of a single soap bubble which maintains the same pressure difference as inside the smaller and outside the larger soap bubble is lesser than the radius of both soap bubbles A and B.
Why coffee runs up into a sugar lump (a small cube of sugar) when one corner of the sugar lump is held in the liquid?
Two spherical rain drops reach the surface of the earth with terminal velocities having ratio 16 : 9. The ratio of their surface area is ______.
Water rises upto a height h in a capillary tube on the surface of the earth. The value of h will increase, if the experimental setup is kept in [g = acceleration due to gravity]
If the surface tension of a soap solution is 3 × 10-2 N/m then the work done in forming a soap film of 20 cm × 5 cm will be ______.
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
The length of a needle floating on water is 2 cm. The additional force due to surface tension required to pull the needle out of water will be (S.T. of water = 7.0 × 10−2 N/m).
The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a ms–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?
The sufrace tension and vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and 2.33 × 103 Pa, respectively. What is the radius of the smallest spherical water droplet which can form without evaporating at 20°C?
Eight droplets of water each of radius 0.2 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the decrease in the surface area.
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
A coaxial cylinder made of glass is immersed in liquid of surface tension ' S'. Radius of inner and outer surface of cylinder are R1 and R2 respectively. Height till which liquid will rise is (Density of liquid is p):
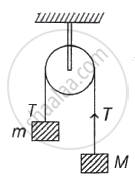
Two blocks of masses m and M are connected by means of a metal wire of cross-sectional area A passing over a frictionless fixed pully as shown in the figure. The system is then released. If M = 2m, then the stress produced in the wire is ______.
Calculate (i) the pressure due to the weight of the water at a depth of 2.5 m and (ii) the depth below the surface of water at which the pressure due to the weight of the water equals 1.0 atm.
Define angle of contact.
