Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
Solution
Internal volume, V = 1 m3 = External volume of the ferry boat
Density of water, \[\rho_w\] = 103 kg/m3
As the weight of the boat is balanced by the buoyant force, we have:
\[\text{mg} = V_1 \times \rho_w \times g\]
\[ \Rightarrow 50 = V_1 \times {10}^3 \]
\[ \Rightarrow V_1 = \frac{5}{100} = 0 . 05 \text{ m}^3\]
(b) Let V2 be the volume of the boat filled with water before water starts coming in from the side.
\[\therefore \text {mg + V}_2 \rho_\text{w} \times \text{g = V} \times \rho_\text{w} \times g [\text{ V is the volume of the water displaced by the boat }. ]\]
\[ \Rightarrow 50 + V_2 \times {10}^3 = 1 \times {10}^3 \]
\[ \Rightarrow V_2 = \frac{{10}^3 - 50}{{10}^3}\]
\[ = \frac{950}{1000} = 0 . 95 \text{ m}^3 \]
Fraction of the boat's volume filled with water\[ = \frac{19}{20}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of semicircular cross section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and on the flat part are in ratio
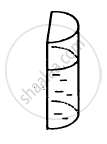
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
Explain the capillary action.
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
The property of _______ of a liquid surface enables the water droplets to move upward in plants.
What are the factors affecting the surface tension of a liquid?
The wear and tear in the machine part is due to ______.
What is surface tension? Explain the applications of surface tension.
Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporisation for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole–1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
- Estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
- Show that the inter–molecular distance for water is `d = [M_A/N_A xx 1/ρ_w]^(1/3)` and find its value.
- 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling point, in the vapour state.
- During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′. Estimate the value of F.
- Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension.
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
In a U-tube, the radii of two columns are respectively r1 and r2. When a liquid of density ρ(θ = 0°) is filled in it, a level difference of h is observed on two arms, then the surface tension of the liquid is ______.
