Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
Solution
As, `h_1/h_2 = r_2/r_1`
∴ h2 = `(h_1r_1)/r_2 = 20 xx r_1/((r_1"/"3)) = 60` mm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Derive Laplace’s law for spherical membrane of bubble due to surface tension.
The surface tension of water at 0°C is 75.5 dyne/cm. Calculate surface tension of water at 25°C.
(α for water = 2.7×10-3/°C)
Define the angle of contact.
Water rises to a height 3.2 cm in a glass capillary tube. Find the height to which the same water will rise in another glass capillary having half area of cross section.
In which of the following substances, surface tension increases with increase in temperature ?
- Copper
- Molten copper
- Iron
- Molten iron
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
Explain why Water on a clean glass surface tends to spread out while mercury on the same surface tends to form drops. (Put differently, water wets glass while mercury does not.)
A body weighs 4.0 kg-wt on the surface of the Earth. What will be its weight on the surface of a plant whose mass is `1/8` th of the mass of the Earth and radius half `(1/2)` of that of the Earth?
Show that the surface tension of a liquid is numerically equal to the surface energy per unit
area.
Calculate the work done in increasing the radius of a soap bubble in air from 1 cm to 2 cm. The surface tension of soap solution is 30 dyne/cm. (Π = 3.142).
The contact angle between pure water and pure silver is 90°. If a capillary tube made of silver is dipped at one end in pure water, will the water rise in the capillary?
When the size of a soap bubble is increased by pushing more air in it, the surface area increases. Does it mean that the average separation between the surface molecules is increased?
Water near the bed of a deep river is quiet while that near the surface flows. Give reasons.
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
By a surface of a liquid we mean
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
If more air is pushed in a soap bubble, the pressure in it
The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
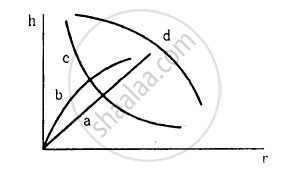
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
Viscosity is a property of
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
Consider a small surface area of 1 mm2 at the top of a mercury drop of radius 4.0 mm. Find the force exerted on this area (a) by the air above it (b) by the mercury below it and (c) by the mercury surface in contact with it. Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Neglect the effect of gravity. Assume all numbers to be exact.
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
Two large glass plates are placed vertically and parallel to each other inside a tank of water with separation between the plates equal to 1 mm. Find the rise of water in the space between the plates. Surface tension of water = 0.075 Nm−1.
Consider an ice cube of edge 1.0 cm kept in a gravity-free hall. Find the surface area of the water when the ice melts. Neglect the difference in densities of ice and water.
A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
Explain the capillary action.
Numerical Problem.
A stone weighs 500 N. Calculate the pressure exerted by it if it makes contact with a surface of area 25 cm2.
A certain number of spherical drops of a liquid of radius R coalesce to form a single drop of radius R and volume V. If T is the surface tension of the liquid, then
Mention the S.I unit and dimension of surface tension.
A drop of oil placed on the surface of water spreads out. But a drop of water place on oil contracts to a spherical shape. Why?
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
Water rises in a capillary tube of radius r upto a height h. The mass of water in a capillary is m. The mass of water that will rise in a capillary of radius `"r"/4` will be ______.
A square frame of each side L is dipped in a soap solution and taken out. The force acting on the film formed is _____.
(T = surface tension of soap solution).
Two spherical rain drops reach the surface of the earth with terminal velocities having ratio 16 : 9. The ratio of their surface area is ______.
If the surface tension of a soap solution is 3 × 10-2 N/m then the work done in forming a soap film of 20 cm × 5 cm will be ______.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
A molecule of water on the surface experiences a net ______.
A water drop of radius R' splits into 'n' smaller drops, each of radius 'r'. The work done in the process is ______.
T = surface tension of water
The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of the water column and 'h' is the height of water in the capillary. The inner circumference of the capillary is ______.
(surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
What is surface tension? Explain the applications of surface tension.
Is surface tension a vector?
If a drop of liquid breaks into smaller droplets, it results in lowering of temperature of the droplets. Let a drop of radius R, break into N small droplets each of radius r. Estimate the drop in temperature.
Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporisation for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole–1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
- Estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
- Show that the inter–molecular distance for water is `d = [M_A/N_A xx 1/ρ_w]^(1/3)` and find its value.
- 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling point, in the vapour state.
- During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′. Estimate the value of F.
- Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension.
A hot air balloon is a sphere of radius 8 m. The air inside is at a temperature of 60°C. How large a mass can the balloon lift when the outside temperature is 20°C? (Assume air is an ideal gas, R = 8.314 J mole–1K–1, 1 atm. = 1.013 × 105 Pa; the membrane tension is 5 Nm–1.)
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
A liquid flows out drop by drop from a vessel through a vertical tube with an internal diameter of 2 mm, then the total number of drops that flows out during 10 grams of the liquid flow out ______. [Assume that the diameter of the neck of a drop at the moment it breaks away is equal to the internal diameter of tube and surface tension is 0.02 N/m].
When an air bubble of radius r rises from the bottom to the surface of a lake, its radius becomes `(5r)/4`. Taking the atmospheric pressure to be equal to the 10 m height of the water column, the depth of the lake would approximately be ______.
(ignore the surface tension and the effect of temperature)
When one end of the capillary is dipped in water, the height of water column is 'h'. The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of water column. The inner circumference of capillary is ______.
(Surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
The surface tension of soap solution is 25 × 10-3 Nm-1. The excess of pressure inside a soap bubble of diameter 1 cm is ______.
The surface tension of boiling water is ______.
A drop of water of radius 8 mm breaks into number of droplets each of radius 1 mm. How many droplets will be formed?
