Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABC is a right angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
उत्तर
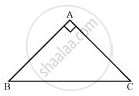
ABC is a right angled triangle in which
∠A = 90°
and AB = AC
In △ABC,
AB = AC
⇒ ∠C = ∠B …(I) ...[Angles opposite to equal sides]
Now, in △ABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° ...[Angle Sum Property of a △)
⇒ 90° + ∠B + ∠B = 180° ...[∵ ∠A = 90° (Given) and ∠B = ∠C from (I)]
⇒ 2∠B = 180° – 90°
⇒ 2∠B = 90°
⇒ ∠B = 45°
Also, ∠C = ∠B
⇒ ∠C = 45°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
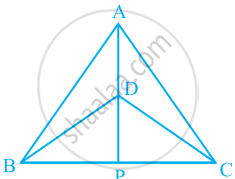
ΔABC and ΔDBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC and vertices A and D are on the same side of BC (see the given figure). If AD is extended to intersect BC at P, show that
- ΔABD ≅ ΔACD
- ΔABP ≅ ΔACP
- AP bisects ∠A as well as ∠D.
- AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
AD is an altitude of an isosceles triangles ABC in which AB = AC. Show that
- AD bisects BC
- AD bisects ∠A
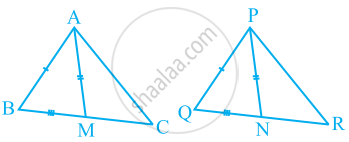
Two sides AB and BC and median AM of one triangle ABC are respectively equal to sides PQ and QR and median PN of ΔPQR (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN
- ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
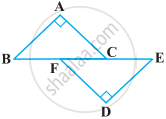
BE and CF are two equal altitudes of a triangle ABC. Using RHS congruence rule, prove that the triangle ABC is isosceles.
In two right triangles one side an acute angle of one are equal to the corresponding side and angle of the other. Prove that the triangles are congruent.
Prove that in a quadrilateral the sum of all the sides is greater than the sum of its diagonals.
In the following figure, BA ⊥ AC, DE ⊥ DF such that BA = DE and BF = EC. Show that ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF.
In a right triangle, prove that the line-segment joining the mid-point of the hypotenuse to the opposite vertex is half the hypotenuse.
Two lines l and m intersect at the point O and P is a point on a line n passing through the point O such that P is equidistant from l and m. Prove that n is the bisector of the angle formed by l and m.
ABC is a right triangle such that AB = AC and bisector of angle C intersects the side AB at D. Prove that AC + AD = BC.
