Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABCD is rectangle formed by the points A(-1, -1), B(-1, 4), C(5, 4) and D(5, -1). If P,Q,R and S be the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively, Show that PQRS is a rhombus.
उत्तर
Here, the points P ,Q, Rand S are the midpoint of ,AB ,BC, CD and DA respectively. Then
`"Coordinates of P = ((-1-1)/2 , (-1+4)/2) = (-1,3/2)`
`"Coordinates of Q = ((-1+5)/2 , (4+4)/2) = (2,.4)`
`"Coordinates of R = ((5+5)/2 , (4-1)/2)= (5,3/2)`
`"Coordinates of " S = ((-1+5)/2 ,(-1-1)/2) = (2,-1)`
Now,
`PQ = sqrt((2+1)^2 +(4-3/2)^2) = sqrt(9+25/4) = sqrt(61/2)`
`QR = sqrt((5-2)^2 +(3/2-4)^2 )= sqrt(9+25/4) = sqrt(61/2)`
`RS = sqrt((5-2)^2 +(3/2+1)^2 )= sqrt(9+25/4) = sqrt(61/2)`
`SP = sqrt((2+1)^2 +(-1-3/2)^2 )= sqrt(9+25/4) = sqrt(61/2)`
` PR = sqrt((5-1)^2 +(3/2-3/2)^2) = sqrt(36) = 6`
`QS = sqrt((2-2)^2 +(-1-4)^2) = sqrt(25) =5`
Thus, PQ = QR = RS = SP and PR ≠ QS therefore PQRS is a rhombus
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If G be the centroid of a triangle ABC, prove that:
AB2 + BC2 + CA2 = 3 (GA2 + GB2 + GC2)
Find the coordinates of the point where the diagonals of the parallelogram formed by joining the points (-2, -1), (1, 0), (4, 3) and(1, 2) meet
Prove that the points A(-4,-1), B(-2, 4), C(4, 0) and D(2, 3) are the vertices of a rectangle.
The line joining the points (2, 1) and (5, -8) is trisected at the points P and Q. If point P lies on the line 2x - y + k = 0. Find the value of k.
If the point A (4,3) and B ( x,5) lies on a circle with the centre o (2,3) . Find the value of x.
Points P, Q, and R in that order are dividing line segment joining A (1,6) and B(5, -2) in four equal parts. Find the coordinates of P, Q and R.
The line segment joining the points A(3,−4) and B(1,2) is trisected at the points P(p,−2) and Q `(5/3,q)`. Find the values of p and q.
ABCD is a rectangle whose three vertices are A(4,0), C(4,3) and D(0,3). Find the length of one its diagonal.
Two points having same abscissae but different ordinate lie on
The perpendicular distance of the point P (4, 3) from x-axis is
If A(3, y) is equidistant from points P(8, −3) and Q(7, 6), find the value of y and find the distance AQ.
If P ( 9a -2 , - b) divides the line segment joining A (3a + 1 , - 3 ) and B (8a, 5) in the ratio 3 : 1 , find the values of a and b .
If the distance between points (x, 0) and (0, 3) is 5, what are the values of x?
What is the area of the triangle formed by the points O (0, 0), A (6, 0) and B (0, 4)?
Find the point on the y-axis which is equidistant from the points (S, - 2) and (- 3, 2).
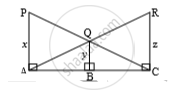
In the above figure, seg PA, seg QB and RC are perpendicular to seg AC. From the information given in the figure, prove that: `1/x + 1/y = 1/z`
If point P is midpoint of segment joining point A(– 4, 2) and point B(6, 2), then the coordinates of P are ______
The line 3x + y – 9 = 0 divides the line joining the points (1, 3) and (2, 7) internally in the ratio ______.
The distance of the point P(2, 3) from the x-axis is ______.
In which quadrant, does the abscissa, and ordinate of a point have the same sign?
