Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
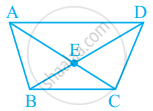
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC. M and N are the mid-points of AD and the respectively. If AB = 12 cm, MN = 14 cm, then CD =
विकल्प
10 cm
12 cm
14 cm
16 cm
उत्तर
The given trapezium ABCD can be drawn as follows:

Here, AB || CD.
M and N are the mid-points of AD and BC respectively.
We have AB = 12cm ,MN = 14cm.
We need to find CD.
Join MN to intersect AC at G.
We have AB || CD and a line MN formed by joining the mid-points of sides AD and BC.
Thus, we can say that MN || AB || CD
In ΔADC M is the mid-point of AD and MG || CD
Therefore, G is the mid point of AC
By using the converse of mid-point theorem, we get:
`MG = 1/2 CD`…… (i)
In ΔABC, N is the mid point of BC and GN || AB
By using the converse of mid-point theorem, we get:
`GN = 1/2 AB` …… (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),we get:
`GN + MG = 1/2AB +1/2 CD`
`MN = 1/2 (AB + CD)`…… (iii)
On substituting AB = 12cm and MN = 14cm in (iii),we get:
`14cm = 1/2(12cm + CD)`
28cm = 12cm + CD
CD = (28 - 12)cm
CD = 16cm
Hence the correct choice is (d).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term Convex Quadrilateral .
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of adjacent angles are there?
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is three times the sum of its exterior angles. Determine the number of sided of the polygon.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ...............
Which of the following quadrilateral is not a rhombus?
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find :
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
Angle A of an isosceles trapezium ABCD is 115°; find the angles B, C and D.
ABCDE is a pentagon in which AB is parallel to DC and ∠A : ∠E : ∠D = 1 : 2 : 3. Find angle A.
In given figure, What is AC – EC?