Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An architecture have model of building. Length of building is 1 m then length of model is 0.75 cm. Then find length and height of model building whose actual length is 22.5 m and height is 10 m
उत्तर
Rough Figure -
| Actual length/height |
Model length/height |
| 1 m | 0.75 cm |
| 22.5 m | ? (x cm) |
| 10 m | ? (y cm) |
The actual length of 1 m is shown as 0.75 cm in the model then let the actual length of 22.5 m is shown in the model by 'x' cm.
`therefore 1/22.5 = 0.75/x`
∴ x = `0.75 xx 22.5`
x = 16.875 cm
Now, The actual length of 1 m is shown as 0.75 cm in the model then let the actual height of 10 m is shown in the model by 'y' cm.
`therefore 1/10 = 0.75/"y"`
∴ y = 0.75 × 10
y = 7.5 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In figure, QA and PB are perpendicular to AB. If AO = 10 cm, BO = 6 cm and PB = 9 cm. Find AQ
E and F are points on the sides PQ and PR, respectively, of a ΔPQR. For the following case, state whether EF || QR:
PE = 4 cm, QE = 4.5 cm, PF = 8 cm and RF = 9 cm
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠DAC, AB = 8 cm, AC = 4 cm and AD = 5 cm.
- Prove that ΔACD is similar to ΔBCA.
- Find BC and CD.
- Find area of ΔACD : area of ΔABC.
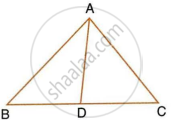
In triangle ABC, AD is perpendicular to side BC and AD2 = BD × DC. Show that angle BAC = 90°.
In the given figure, AB || EF || DC; AB = 67.5 cm, DC = 40.5 cm and AE = 52.5 cm.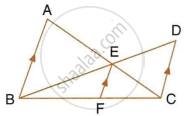
- Name the three pairs of similar triangles.
- Find the lengths of EC and EF.
A line PQ is drawn parallel to the base BC of ∆ABC which meets sides AB and AC at points P and Q respectively. If AP = `1/3` PB; find the value of:
- `"Area of ΔABC"/"Area of ΔAPQ"`
- `"Area of ΔAPQ"/"Area of trapezium PBCQ"`
In an isosceles ΔABC, the base AB is produced both ways in P and Q such that
AP × BQ = AC2.
Prove that ΔACP~ΔBCQ.

ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and their areas are respectively `100cm^2` and `49cm2`. If the altitude of ΔABC is 5cm, find the corresponding altitude of ΔDEF.
In the given figure, X is any point in the interior of triangle. Point X is joined to vertices of triangle. Seg PQ || seg DE, seg QR || seg EF. Fill in the blanks to prove that, seg PR || seg DF.
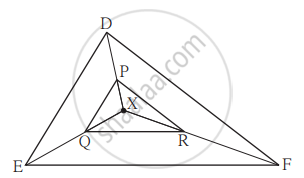
Proof : In ΔXDE, PQ || DE ...`square`
∴ `"XP"/square = square/"QE"` ...(I) (Basic proportionality theorem)
In ΔXEF, QR || EF ...`square`
∴ `square/square = square/square ..."(II)" square`
∴ `square/square = square/square` ...from (I) and (II)
∴ seg PR || seg DF ...(converse of basic proportionality theorem)
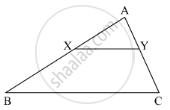
In the given figure, seg XY || seg BC, then which of the following statements is true?
In Δ PQR, MN is drawn parallel to QR. If PM = x, MQ = (x-2), PN = (x+2) and NR = (x-1), find the value of x.
A triangle LMN has been reduced by scale factor 0.8 to the triangle L' M' N'. Calculate: the length of M' N', if MN = 8 cm.
A triangle LMN has been reduced by scale factor 0.8 to the triangle L' M' N'. Calculate: the length of LM, if L' M' = 5.4 cm.
A triangle ABC is enlarged, about the point O as centre of enlargement, and the scale factor is 3. Find : OA, if OA' = 6 cm.
In ΔABC, D and E are the points on sides AB and AC respectively. Find whether DE || BC, if AB = 6.3 cm, EC = 11.0 cm, AD = 0.8 cm and AE = 1.6 cm.
In the adjacent figure, ∆ABC is right angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE and hence find the lengths of AE and DE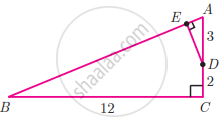
ΔPQR ~ ΔSUV. Write pairs of congruent angles
Observe the figure and complete the following activity
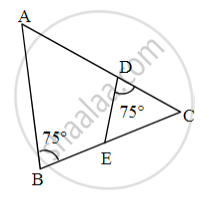
In fig, ∠B = 75°, ∠D = 75°
∠B ≅ [ ______ ] ...[each of 75°]
∠C ≅ ∠C ...[ ______ ]
ΔABC ~ Δ [ ______ ] ...[ ______ similarity test]
In ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. A then ______.
In ΔPQR, S and T are points on PQ and PR respectively. `(PS)/(SQ) = (PT)/(TR)` and ∠PST = ∠PRQ. Prove that PQR is an isosceles triangle.
