Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image ______.
विकल्प
moves away from the lens with an uniform speed 5 m/s.
moves away from the lens with an uniform accleration.
moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
moves towards the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
उत्तर
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
Explanation:
In our problem the object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed of 5 m/s, hence the image will move away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration, the image moves slower in the beginning and faster later on will move from F to 2F and when the object moves from 2F to F, the image will move from 2F to infinity. At 2F, the speed of the object and image will be equal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is
- a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, and
- a concave lens of focal length 16 cm?
You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
- Determine the ‘effective focal length’ of the combination of the two lenses, if they are placed 8.0 cm apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of the effective focal length of this system useful at all?
- An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system and the size of the image.
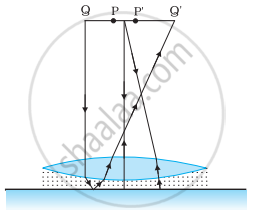
Figure shows an equiconvex lens (of refractive index 1.50) in contact with a liquid layer on top of a plane mirror. A small needle with its tip on the principal axis is moved along the axis until its inverted image is found at the position of the needle. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured to be 45.0 cm. The liquid is removed and the experiment is repeated. The new distance is measured to be 30.0 cm. What is the refractive index of the liquid?
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
A convex lens forms a real image of a point object placed on its principals axis. If the upper half of the lens is painted black,
(a) the image will be shifted downward
(b) the image will be shifted upward
(c) the image will not be shifted
(d) the intensity of the image will decrease.
A small piece of wood is floating on the surface of a 2.5 m deep lake. Where does the shadow form on the bottom when the sum is just setting? Refractive index of water = 4/3.
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
In many experimental set-ups the source and screen are fixed at a distance say D and the lens is movable. Show that there are two positions for the lens for which an image is formed on the screen. Find the distance between these points and the ratio of the image sizes for these two points.
Show that the least possible distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
