Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following.
Describe the structure of the Ozone. Give two uses of ozone.
उत्तर
Structure of ozone:
Ozone (O3) is an angular molecule. The two O – O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are identical, 128 pm, and the O – O – O bond angle of about 117°. It is a resonance hybrid of two canonical forms.
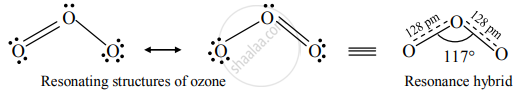
Uses of ozone:
- Ozone is used for air purification at crowded places like cinema halls, tunnels, railways, etc.
- In sterilizing drinking water by oxidising all germs and bacteria.
- For bleaching ivory, oils, starch, wax and delicate fabrics such as silk.
- In the manufacture of synthetic camphor, potassium permanganate, etc.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Ozone layer is depleted by ______.
Answer the following.
What happens when nitric oxide reacts with ozone.
Answer the following.
Draw structures of XeF6
Answer the following.
Draw structures of XeO3
Answer the following.
Draw structures of XeF2
What are interhalogen compounds?
O2 molecule is ______.
The number of covalent bonds present in sulfuric acid:
Complete the following reaction:
\[\ce{SO_{2(g)} + Cl_{2(g)} ->[Charcoal]}\] ?
Draw resonance hybrid structure of SO2 in two canonical forms.
Which of the following molecule does not contain oxygen?
Which among the following oxides of nitrogen is called nitrogen sesquioxide?
Find the CORRECT statement.
\[\ce{I2_{(g)} + H2S_{(g)} -> 2HI_{(g)} + S_{(s)}}\]
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
What is the colour of gaseous ozone?
High concentration of which of the following in the atmosphere leads to stiffness of flower buds which eventually fall off from plants?
What will be the formula of an oxide of iodine (atomic mass = 127) which contains 25.4 g of iodine and 8g of oxygen?
Write balanced equation of a reaction in which ozone reduces hydrogen peroxide.
Write any two characteristics of interhalogen compounds.
Write the reaction of the following with concentrated H2SO4:
NaCl
Write the reaction of the following with concentrated H2SO4:
KNO3
Industrial method of preparation of dioxygen.
