Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following.
Describe the structure of the Ozone. Give two uses of ozone.
Solution
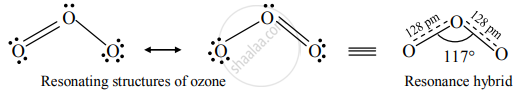
Structure of ozone:
Ozone (O3) is an angular molecule. The two O – O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are identical, 128 pm, and the O – O – O bond angle of about 117°. It is a resonance hybrid of two canonical forms.
Uses of ozone:
- Ozone is used for air purification at crowded places like cinema halls, tunnels, railways, etc.
- In sterilizing drinking water by oxidising all germs and bacteria.
- For bleaching ivory, oils, starch, wax and delicate fabrics such as silk.
- In the manufacture of synthetic camphor, potassium permanganate, etc.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Ozone layer is depleted by ______.
What happens when lead sulfide reacts with ozone \[\ce{O3}\]?
Discuss the structure of sulfur dioxide.
Answer the following.
Draw structures of XeO3
Answer the following.
Draw structures of XeOF4
What are interhalogen compounds?
Answer the following.
How are XeO3 and XeOF4 prepared?
O2 molecule is ______.
The number of covalent bonds present in sulfuric acid:
What is the O−S−O bond angle in SO2?
Identify the INCORRECT match.
Which among the following oxides of nitrogen is called nitrogen sesquioxide?
Find the CORRECT statement.
\[\ce{I2_{(g)} + H2S_{(g)} -> 2HI_{(g)} + S_{(s)}}\]
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
What is the colour of gaseous ozone?
Mark the oxide which is amphoteric in character.
Identify the element that forms amphoteric oxide.
Give reason:
Bleaching action of ozone is also called dry bleach.
Write balanced equation of a reaction in which ozone reduces hydrogen peroxide.
Write any two characteristics of interhalogen compounds.
What are the basic oxides? Explain with an example.
Electrolytic method of preparation of dioxygen.
Industrial method of preparation of dioxygen.
