Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Show that its time period is given by, 2π`sqrt((l cos theta)/("g"))` where l is the length of the string, θ is the angle that the string makes with the vertical, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
उत्तर
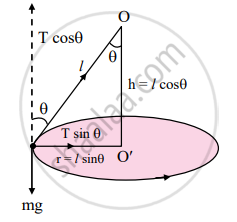
Conical pendulum
Where,
O: rigid support,
T: tension in the string,
l: length of string,
h: height of support from bob,
v: velocity of bob,
r: radius of horizontal circle,
θ: semi-vertical angle,
mg: weight of bob
- Consider a bob of mass m tied to one end of a string of length ‘l’ and the other end is fixed to a rigid support.
- Let the bob be displaced from its mean position and whirled around a horizontal circle of radius ‘r’ with constant angular velocity ω, then the bob performs U.C.M.
- During the motion, string is inclined to the vertical at an angle θ as shown in the figure above.
- In the displaced position, there are two forces acting on the bob.
a. The weight mg acting vertically downwards.
b. The tension T acting upward along the string. - The tension (T) acting in the string can be resolved into two components:
a. T cos θ acting vertically upwards.
b. T sin θ acting horizontally towards centre of the circle. - Since there is no net force, the vertical component T cos θ balances the weight and the horizontal component T sin θ provides the necessary centripetal force.
∴ T cos θ = mg ....(1)
T sin θ = `"mv"^2/"r" = "mr"omega^2` ....(2) - Dividing equation (2) by (1),
tan θ = `"v"^2/"rg"` ....(3)
Therefore, the angle made by the string with the vertical is θ = tan-1 `("v"^2/"rg")` - Since we know v = `(2pi"r")/"T"`
∴ tan θ = `(4pi^2"r"^2)/("T"^2"rg")` ....[From (3)]
T = `2pi sqrt("r"/("g"tan theta))`
T = `2pi sqrt((l sin theta)/("g"tan theta)) ....[because "r" = l sin theta]`
T = `2pi sqrt((l cos theta)/("g"))`
T = `2pi sqrt("h"/"g")` .....(∵ h = l cos θ)
where l is length of the pendulum and h is the vertical distance of the horizontal circle from the fixed point O.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In U. C. M (Uniform Circular Motion), prove the relation `vec v = vec w xx vec r`, where symbols have their usual meanings.
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point.
A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 s with a velocity of 10.0 `hatj "m/s"` and moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of `(8.0 hati + 2.0 hatj) ms^(-2)`.
- At what time is the x-coordinate of the particle 16 m? What is the y-coordinate of the particle at that time?
- What is the speed of the particle at the time?
A uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. Explain it. State whether the acceleration is uniform or variable? Name the force responsible to cause this acceleration. What is the direction of force at any instant? Draw a diagram in support of your answer.
A piece of stone tied at the end of a thread is whirled in a horizontal circle with uniform speed by hand. Answer the following questions:
- Is the velocity of stone uniform or variable?
- Is the acceleration of stone uniform or variable?
- What is the direction of acceleration of stone at any instant?
- Which force provides the centripetal force required for circular motion?
- Name the force and its direction which acts on the hand.
State True or False
The earth moves around the sun with a uniform.
A uniform linear motion is unaccelerated, while a uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed continuously changes because of the direction of motion changes.
Which of the following quantity remains constant in uniform circular motion:
Answer the following question.
Define angular velocity.
Answer the following question.
Show that the centripetal force on a particle undergoing uniform circular motion is -mrω2.
Solve the following problem.
A particle moves in a circle with a constant speed of 15 m/s. The radius of the circle is 2 m. Determine the centripetal acceleration of the particle.
Which of the following graph represents uniform motion of a moving particle?
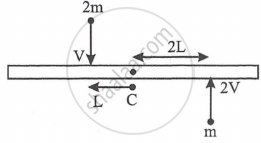
A uniform rod of length '6L' and mass '8 m' is pivoted at its centre 'C'. Two masses 'm' and ' 2m' with speed 2v, v as shown strikes the rod and stick to the rod. Initially the rod is at rest. Due to impact, if it rotates with angular velocity 'w1' then 'w' will be ________.
The ratio of angular speed of a hour-hand to the second-hand of a watch is ____________.
The ratio of the angular speed of minute hand and hour hand of a watch is ____________.
A particle of mass m is executing uniform circular motion on a path of radius r. If p is the magnitude of its linear momentum, the radial force acting on the particle is ______.
Consider a simple pendulum of length 4 m. Its bob performs a circular motion in horizontal plane with its string making an angle 60° with the vertical. The Period of rotation of the bob is ____________.(Take g = 10 m/s2)
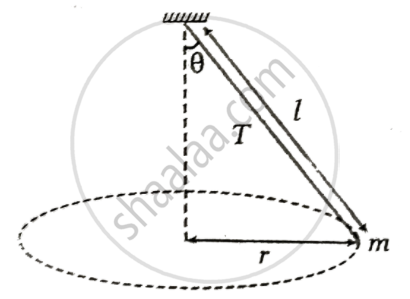
A string of length 'l' fixed at one end carries a mass 'm' at the other end. The string makes `3/pi` revolutions/second around the vertical axis through the fixed end as shown in figure. The tension 'T' in the string is ______.
A body moves in a uniform circular motion ______.
A body is said to be in nonuniform motion if it travels ______.
In uniform motion, an object travels equal ______ in ______ interval of time.
For a particle performing uniform circular motion, choose the correct statement(s) from the following:
- Magnitude of particle velocity (speed) remains constant.
- Particle velocity remains directed perpendicular to radius vector.
- Direction of acceleration keeps changing as particle moves.
- Angular momentum is constant in magnitude but direction keeps changing.
Earth also moves in circular orbit around sun once every year with on orbital radius of 1.5 × 1011 m. What is the acceleration of earth (or any object on the surface of the earth) towards the centre of the sun? How does this acceleration compare with g = 9.8 m/s2?
A small bead of mass m can move on a smooth circular wire (radius R) under the action of a force F = `"Km"/"r"^2` directed (r = position of bead r from P and K = constant) towards a point P within the circle at a distance R/2 from the centre. The minimum velocity should be ______ m/s of bead at the point of the wire nearest the centre of force (P) so that bead will complete the circle. (Take `"k"/(3"R")` = 8 unit)

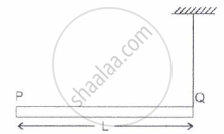
A rod PQ of mass M and length L is hinged at end P. The rod is kept horizontal by a massless string tied to point Q as shown in figure. When string is cut, the initial angular acceleration of the rod is ______.
Angular speed of hour hand of a clock in degree per second is ______.
The kinetic energy K of a particle moving along a circle of radius R depends on the distance covered s as K = as2, where a is a constant. The force acting on the particle is ______.
