Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In U. C. M (Uniform Circular Motion), prove the relation `vec v = vec w xx vec r`, where symbols have their usual meanings.
उत्तर
Analytical method :
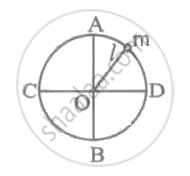
Consider a particle revolving in the anticlockwise sense along the circumference of a circle of radius r with centre O as shown.

Let
`vec omega`= angular velocity of the particle
`vec v`= linear velocity of the particle
`vec r`= radius of the particle
In the vector form, the linear dispalcement is
`vec (delta s) = vec (delta theta) times vec r`
Dividing both sides by `delta t` we get
`vec (delta s)/(delta t) = vec (delta theta)/(delta t) times vec r`
`lim_(delta t -> 0) vec (delta s)/(delta t) = lim_(delta t -> 0) vec (delta theta)/(delta t) times vec r`
`therefore vec(dS)/dt = vec(d theta)/(delta t) times vec r`
but
`vec(dS)/dt = vec v` = Linear velocity
`vec(d theta)/(delta t) = vec omega` = angular velocity
`therefore vec v = vec omega times vec r`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A particle rotates in U.C.M. with tangential velocity V along a horizontal circle of diameter ‘D' . Total angular displacement of the particle in time 't' is..........
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Compare its centripetal acceleration with the acceleration due to gravity.
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27 km/h. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 80 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate of 0.50 m/s every second. What is the magnitude and direction of the net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn?
Draw a neat labelled diagram for a particle moving in a circular path with a constant speed. In you diagram show the direction of velocity at any instant.
Differentiate between uniform linear motion and uniform circular motion.
A piece of stone tied at the end of a thread is whirled in a horizontal circle with uniform speed by hand. Answer the following questions:
- Is the velocity of stone uniform or variable?
- Is the acceleration of stone uniform or variable?
- What is the direction of acceleration of stone at any instant?
- Which force provides the centripetal force required for circular motion?
- Name the force and its direction which acts on the hand.
| A small pebble tied at one end of a string is placed near the periphery of a circular disc, at the centre of which the other end of the string is tied to a peg. The disc is rotating about an axis passing through its centre. |
- What will be your observation when you are standing outside the disc? Explain.
- What will be your observation when you are standing at the centre of the disc? Explain.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed continuously changes because of the direction of motion changes.
Complete a sentence and explain it.
When an object is in uniform circular motion, its ______ changes at every point.
Solve the following problem.
A car moves in a circle at a constant speed of 50 m/s and completes one revolution in 40 s. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car.
Solve the following problem.
A projectile is thrown at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. What should be the range of initial velocity (u) so that its range will be between 40m and 50 m? Assume g = 10 m s-2.
Which of the following graph represents uniform motion of a moving particle?
What is meant by uniform circular motion? Give two examples of uniform circular motion.
If a particle moves with uniform speed then its tangential acceleration will be ______.
A small sphere is attached to a cord and rotates in a vertical circle about a point O. If the average speed of the sphere is increased, the cord is most likely to break at the orientation when the mass is at ____________.
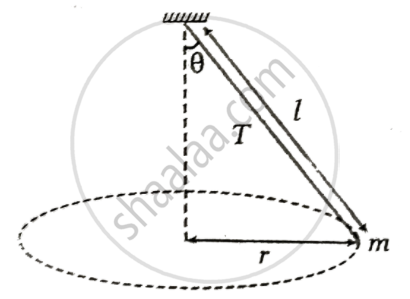
Consider a simple pendulum of length 4 m. Its bob performs a circular motion in horizontal plane with its string making an angle 60° with the vertical. The Period of rotation of the bob is ____________.(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A body of mass ·m' is moving along a circle of radius 'r' with linear speed 'v'. Now, to change the linear speed to `V/2` and to move it along the circle of radius '4r', required change in the centripetal force of the body is ______.
A string of length 'l' fixed at one end carries a mass 'm' at the other end. The string makes `3/pi` revolutions/second around the vertical axis through the fixed end as shown in figure. The tension 'T' in the string is ______.
A mass 'm' is tied to one end of a spring and whirled in a horizontal circle with constant angular velocity. The elongation in the spring is 1 cm. If the angular speed is doubled, the elongation in the spring is 6 cm. The original length of the spring is ______.
A stone of mass 3 kg attached at one end of a 2m long string is whirled in horizontal circle. The string makes an angle of 45° with the vertical then the centripetal force acting on the string is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2 , tan 45° = 1)
A string of length `l` is fixed at one end and carries a mass 'm' at the other end. The mass is revolving along a horizontal circle of radius 'r' making 'θ' as the semi-vertical angle of cone and `(1/pi)` revolutions per second around the vertical axis through fixed end. The tension in the string is ______.
A body moves in a uniform circular motion ______.
The motion of the bus is ______ motion.
If a body is moving in a circle of radius r with a constant speed v, its angular velocity is ______.
A small bead of mass m can move on a smooth circular wire (radius R) under the action of a force F = `"Km"/"r"^2` directed (r = position of bead r from P and K = constant) towards a point P within the circle at a distance R/2 from the centre. The minimum velocity should be ______ m/s of bead at the point of the wire nearest the centre of force (P) so that bead will complete the circle. (Take `"k"/(3"R")` = 8 unit)

A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is v at the end of second revolution, after the revolution has started, then the tangential acceleration is ______.
A wheel is rotating at 900 rpm about its axis. When the power is cut off it comes to rest in 1 min. The angular retardation (assumed to be uniform (in rad s-1) is ______.
Explain the meaning of uniform circular motion.
