Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
What are the dimensions of the universal gravitational constant?
उत्तर
The dimensions of universal gravitational constant are: [L3M-1T-2].
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
Answer the following:
You can shield a charge from electrical forces by putting it inside a hollow conductor. Can you shield a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter by putting it inside a hollow sphere or by some other means?
Choose the correct alternative:
Acceleration due to gravity is independent of mass of the earth/mass of the body.
How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 1.5 × 108 km.
Universal law of gravitation states that every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. If this is true, why don’t we notice such forces ? Why don’t the two objects in a room move towards each other due to this force ?
Can two particles be in equilibrium under the action of their mutual gravitational force? Can three particles be? Can one of the three particles be?
Can you think of two particles which do not exert gravitational force on each other?
A person sitting in a chair in a satellite feels weightless because
Inside a uniform spherical shell
(a) the gravitational potential is zero
(b) the gravitational field is zero
(c) the gravitational potential is same everywhere
(d) the gravitational field is same everywhere
Derive an expression for the gravitational field due to a uniform rod of length L and mass M at a point on its perpendicular bisector at a distance d from the centre.
A particle of mass 100 g is kept on the surface of a uniform sphere of mass 10 kg and radius 10 cm. Find the work to be done against the gravitational force between them to take the particle away from the sphere.
Explain the following:
People often shake the branches of a tree for getting down its fruits.
State whether the gravitational force between two masses is attractive or repulsive ?
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Made four times
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Almost zero
Why don't you feel the force of attraction between your friend sitting close to you and yourself?
Where will you weigh more: at the moon's surface or at the earth's surface?
A force can produce ________, In an object at rest. It can __________ an object and change its __________ of motion.
What does a force do in the following case?
You catch a kicked ball.
Two equal and opposite forces acting at the same point on a stationary body. Will the body move? Give reason to explain your answer.
State Newton's law of gravitation. What is the difference between:
g and G?
The distance-time values for an object moving along straight line are given below:
| Time (s) | Distance (m) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 27 |
Answer the following question.
State Newton’s law of gravitation and express it in vector form.
Solve the following problem.
Find the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth.
Given Mass of the Sun = 1.99 × 1030 kg
Mass of the Earth = 5.98 × 1024 kg
The average distance between the Earth and the Sun = 1.5 × 1011 m.
For the weight of body of mass 5 kg to be zero on equator of the earth, angular velocity of the earth must be (The radius of earth = 6400 km, acceleration due to gravity = 10 m/s2).
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

If the law of gravitation, instead of being inverse-square law, becomes an inverse-cube law- ______.
- planets will not have elliptic orbits.
- circular orbits of planets is not possible.
- projectile motion of a stone thrown by hand on the surface of the earth will be approximately parabolic.
- there will be no gravitational force inside a spherical shell of uniform density.
The gravitational force between a hollow spherical shell (of radius R and uniform density) and a point mass is F. Show the nature of F vs r graph where r is the distance of the point from the centre of the hollow spherical shell of uniform density.
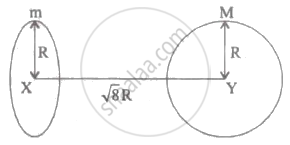
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If `sqrt8` R is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass 'm')and a sphere (mass 'M') where both have equal radius 'R'.
Newton's universal law of gravitation applies to ______.
