Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive an expression for the gravitational field due to a uniform rod of length L and mass M at a point on its perpendicular bisector at a distance d from the centre.
उत्तर
Consider a small mass element of length dx at a distance x from the centre of the rod.
Mass of the mass element, dm = (M/L) × dx
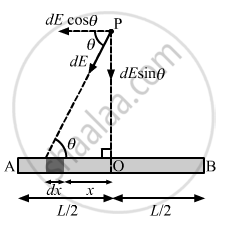
Gravitational field due to this element at point P is given by
The components of the gravitational field due to the symmetrical mass element along the length of the rod cancel each other.
Now, resultant gravitational field = 2dE sin θ
Total gravitational field due to the rod at point P is given by
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
If you compare the gravitational force on the Earth due to the Sun to that due to the Moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the Moon’s pull. (You can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the Moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of Sun. Why?
Write the three laws given by Kepler. How did they help Newton to arrive at the inverse square law of gravity?
Can you think of two particles which do not exert gravitational force on each other?
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Almost zero
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Calculate the time it takes to reach this height.
Where will you weigh more: at the centre of the earth or at the surface of the earth?
What does a force do in the following case?
You pull the skin of your arm
You can change the direction in which an object is moving by___________.
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
A person walking on the ground.
State the law of gravitation. Why is it called universal?
Gravity is another kind of ________. It exerts all through the ________. The Sun's gravity keeps the ___________ in their orbits. Gravity can only be felt with very large ________.
Is there a gravitational attraction between you and the book? Explain.
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
What do you mean by a gravitational constant?
State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Express it with the mathematical form of force of gravitation?
Different points in earth are at slightly different distances from the sun and hence experience different forces due to gravitation. For a rigid body, we know that if various forces act at various points in it, the resultant motion is as if a net force acts on the c.m. (centre of mass) causing translation and a net torque at the c.m. causing rotation around an axis through the c.m. For the earth-sun system (approximating the earth as a uniform density sphere).
Shown are several curves (Figure). Explain with reason, which ones amongst them can be possible trajectories traced by a projectile (neglect air friction).
