Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you mean by a gravitational constant?
उत्तर
- From Newton’s law of gravitation,
F = G`("m"_1"m"_2)/"r"^2`
where, G = constant called universal gravitational constant. Its value is 6.67 × 10-11 N m2/kg2. - G = `"Fr"^2/("m"_1"m"_2)`
If m1 = m2 = 1 kg, r = 1 m then F = G.
Hence, the universal gravitational constant is the force of gravitation between two particles of unit mass separated by unit distance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m).
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
A rocket is fired from the earth towards the sun. At what distance from the earth’s centre is the gravitational force on the rocket zero? Mass of the sun = 2 ×1030 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg. Neglect the effect of other planets etc. (orbital radius = 1.5 × 1011 m).
How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 1.5 × 108 km.
Write the three laws given by Kepler. How did they help Newton to arrive at the inverse square law of gravity?
A body is suspended from a spring balance kept in a satellite. The reading of the balance is W1 when the satellite goes in an orbit of radius R and is W2 when it goes in an orbit of radius 2 −R.
A semicircular wire has a length L and mass M. A particle of mass m is placed at the centre of the circle. Find the gravitational attraction on the particle due to the wire.
A solid sphere of mass m and radius r is placed inside a hollow thin spherical shell of mass M and radius R as shown in the following figure . A particle of mass m' is placed on the line joining the two centres at a distance x from the point of contact of the sphere and the shell. Find the magnitude of the resultant gravitational force on this particle due to the sphere and the shell if (a) r < x < 2r, (b) 2r < x < 2R and (c) x > 2R.
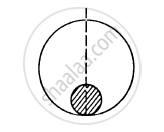
A particle of mass 100 g is kept on the surface of a uniform sphere of mass 10 kg and radius 10 cm. Find the work to be done against the gravitational force between them to take the particle away from the sphere.
Explain the following:
People often shake the branches of a tree for getting down its fruits.
State whether the gravitational force between two masses is attractive or repulsive ?
Define one Newton. How much maximum acceleration can it produce in a mass of 1 kg?
The acceleration produced by a force in an object is directly proportional to the applied _________ And inversely proportional to the _________ Of the object.
Who stated the law of gravitation?
Distinguish between gravity and gravitation
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Doubled
What is meant by the equation :
`g= Gxxm/r^2`
where the symbols have their usual meanings.
A force can produce ________, In an object at rest. It can __________ an object and change its __________ of motion.
Explain why:
The atmosphere does not escape.
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
The distance-time values for an object moving along straight line are given below:
| Time (s) | Distance (m) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 27 |
Answer the following question.
State Newton’s law of gravitation and express it in vector form.
The _______ force is much weaker than other forces in nature.
Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
The gravitational force between a hollow spherical shell (of radius R and uniform density) and a point mass is F. Show the nature of F vs r graph where r is the distance of the point from the centre of the hollow spherical shell of uniform density.
Answer the following questions in reference to the figure below:
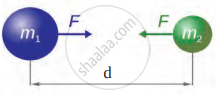
- Which relation is shown in the figure?
- What will happen if the mass of one of the objects is doubled?
