Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you mean by a gravitational constant?
उत्तर
- From Newton’s law of gravitation,
F = G`("m"_1"m"_2)/"r"^2`
where, G = constant called universal gravitational constant. Its value is 6.67 × 10-11 N m2/kg2. - G = `"Fr"^2/("m"_1"m"_2)`
If m1 = m2 = 1 kg, r = 1 m then F = G.
Hence, the universal gravitational constant is the force of gravitation between two particles of unit mass separated by unit distance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
State and explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion. Draw diagrams to illustrate these laws.
Universal law of gravitation states that every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. If this is true, why don’t we notice such forces ? Why don’t the two objects in a room move towards each other due to this force ?
Can you think of two particles which do not exert gravitational force on each other?
Let V and E be the gravitational potential and gravitational field at a distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical shell. Consider the following two statements :
(A) The plot of V against r is discontinuous.
(B) The plot of E against r is discontinuous.
Consider a planet moving in an elliptical orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet by the gravitational force of the sun
(a) is zero in any small part of the orbit
(b) is zero in some parts of the orbit
(c) is zero in one complete revolution
(d) is zero in no part of the motion.
Three equal masses m are placed at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side a. Find the force exerted by this system on another particle of mass m placed at (a) the mid-point of a side, (b) at the centre of the triangle.
Two small bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg are kept a distance 1.0 m apart and released. Assuming that only mutual gravitational forces are acting, find the speeds of the particles when the separation decreases to 0.5 m.
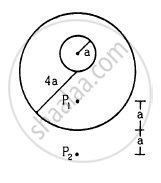
A uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and radius 4a (In the following figure). The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the inner sphere. Find the gravitational field at the points P1 and P2 shown in the figure.
The gravitational field in a region is given by \[E = \left( 2 \overrightarrow{i} + 3 \overrightarrow{j} \right) N {kg}^{- 1}\] . Show that no work is done by the gravitational field when a particle is moved on the line 3y + 2x = 5.
[Hint : If a line y = mx + c makes angle θ with the X-axis, m = tan θ.]
State whether the gravitational force between two masses is attractive or repulsive ?
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The mass of earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of earth is 6.4 × 106 m. The magnitude of force between the mass of 1 kg and the earth is:
The acceleration produced by a force in an object is directly proportional to the applied _________ And inversely proportional to the _________ Of the object.
What is meant by the equation :
`g= Gxxm/r^2`
where the symbols have their usual meanings.
A force can produce ________, In an object at rest. It can __________ an object and change its __________ of motion.
Two equal and opposite forces acting at the same point on a stationary body. Will the body move? Give reason to explain your answer.
What is the difference between gravity and gravitation?
State Newton's law of gravitation. What is the difference between:
g and G?
Show that gravity decreases at higher altitudes.
The _______ force is much weaker than other forces in nature.
State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Express it with the mathematical form of force of gravitation?
Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

Molecules in air in the atmosphere are attracted by gravitational force of the earth. Explain why all of them do not fall into the earth just like an apple falling from a tree.
Complete the chart below.
| F(N) | M1(kg) | M2(kg) | D(m) |
| (a) | 50 | 84 | 02 |
| 16 × 109 | 1.63 × 1022 | (b) | 34 |
Four identical particles of equal masses 1 kg made to move along the circumference of a circle of radius 1 m under the action of their own mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle will be ______.
Newton's universal law of gravitation applies to ______.
