Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
उत्तर
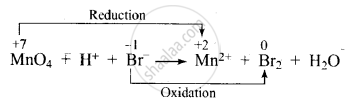
Dividing the equation into two half-reactions:
Oxidation half-reaction: \[\ce{Br^{-} -> Br2}\]
Reduction half-reaction: \[\ce{MnO^{-}4 -> Mn^{2+}}\]
Balancing oxidation and reduction half-reactions separately as:
Oxidation half-reaction:
\[\ce{Br^{-} -> Br2}\]
\[\ce{2Br^{-} -> Br2}\]
\[\ce{2Br^{-} -> Br2 + 2e-}\] .....(i)
Reduction half-reaction:
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 -> Mn^{2+}}\]
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + 5e^{-} -> Mn^{2+}}\]
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + 8H^{+} + 5e^{-} -> Mn^{2+}}\]
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + 8H^{+} + 5e^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + 4H2O}\] .....(ii)
To balance the electrons, multiply equation (i) by 5 and equation (ii) by 2 and add
\[\ce{2MnO^{-}4 + 10Br^{-} + 16H^{+} -> 2Mn^{2+} + 5Br2 + 8H2O}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` and `"NO"_3^-`. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
Whenever a reaction between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. Justify this statement giving three illustrations.
Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + I– (aq) → MnO2 (s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)}\]
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + SO2 (g) → Mn^{2+} (aq) + HSO-_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{H2O2 (aq) + Fe^{2+} (aq) → Fe^{3+} (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{Cr_2O^{2-}_7 + SO2(g) → Cr^{3+} (aq) + SO^{2-}_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
Justify that the following reaction is redox reaction; identify the species oxidized/reduced, which acts as an oxidant and which acts as a reductant.
\[\ce{2Cu2O_{(S)} + Cu2S_{(S)}->6Cu_{(S)} + SO2_{(g)}}\]
Identify the oxidising agent in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH4_{(g)} + 2O2_{(g)} -> CO2_{(g)} + 2H2O_{(l)}}\]
When methane is burnt completely, oxidation state of carbon changes from ______.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Reaction of liquid hydrazine \[\ce{(N2H4)}\] with chlorate ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}3)}\] in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Dichlorine heptaoxide \[\ce{(Cl2O7)}\] in gaseous state combines with an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide in acidic medium to give chlorite ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}2)}\] and oxygen gas. (Balance by ion-electron method)
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO2 + C2O^{2-}4 -> Mn^{2+} + CO2}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) -> 3HCl (aq) + H3PO3 (aq)}\]
