Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group:
विकल्प
carboxylic acid
aldehyde
ketone
alcohol
उत्तर
ketone
Explanation:
The structure of butanone is:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.......}||\\
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
It has \[\ce{>C = O}\] (Ketone group) as its functional group.
संबंधित प्रश्न
List three characteristic properties of covalent compounds.
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The form of carbon which is known as black lead is ...........
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
In forming N2 molecule, .............. electrons are shared by each atom of nitrogen.
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
The number of single covalent bonds in C2H2 molecule are ...........
What type of chemical bonds are formed by carbon? Why?
Give one example, state what are covalent compounds?
How will you find out which of the water soluble compound A or B is ionic?
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
Al and Cl2
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
K and H
The solution of one of the following compounds will not conduct electricity. This compounds is:
(a) NaCl
(b) CCl4
(c) MgCl2
(d) CaCl2
What are the conditions necessary for the formation of covalent molecules?
What do you understand by polar covalent compounds?
State the type of bonding in the following molecule.
Water
Complete the following:
When the nuclei of two different reacting atoms are of ______ mass, then a bond so formed is called ______ covalent bond. (equal, unequal, polar, non-polar)
Give two example in following case:
Solid covalent compounds
Give two example in following case:
Liquid non polar compounds
Observe the straight chain hydrocarbons given below and answer the following
questions :
i) Which of the straight chain compounds from A and B is saturated and unsaturated straight chains?
ii) Name these straight chains.
iii) Write their chemical formulae and number of – CH2 - units.

Molecular formula of Propane is C3H8 , write the structural formula of propane.
Give examples for the following:
Two liquid non polar compounds.
Give examples for the following:
Two gaseous polar compounds.
Explain the structure of Hydronium ion.
The following table shows the electronic configuration of the elements W, X, Y, Z:
|
Element |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
|
Electronic |
2,8,1 |
2,8,7 |
2,5 |
1 |
Answer the following questions based on the table above:
What type of bond is formed between Y and Z.
Explain why carbon tetrachloride does not dissolve in water.
Draw the electron dot diagram and structure of :
methane
State the type of bond formed, and draw Lewis structure of water.
Name two compounds that are covalent when taken pure but produce ions when dissolved in water.
Taking MgCl2 as an electrovalent compound, CCl4 as a covalent compound, give four difference between electrovalent and covalent compounds
Potassium chloride is an electrovalent compound, while hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound, But, both conduct electricity in their aqueous solutions. Explain.
The molecular masses of a carbon compound spread over a range of _______.
Write an Explanation.
Alkane
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc}\phantom{......}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\ \phantom{.....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - C = C}\\\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.........}|\\ \phantom{.....}\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{H}\end{array}\] |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
 |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
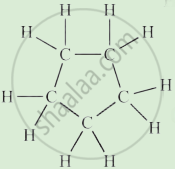 |
Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless, odourless gas Y was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water, which turned milky. It was concluded that ______.
The table shows the electronic structures of four elements.
| Element | Electronic Structure |
| P | 2, 6 |
| Q | 2, 8, 1 |
| R | 2, 8, 7 |
| S | 2, 8, 8 |
- Identify which element(s) will form covalent bonds with carbon.
- “Carbon reacts with an element in the above table to form several compounds.” Give suitable reason.
The number of single and double bonds present in a molecule of benzene (C6H6) respectively, are ______.
In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to ______ of electrons.
