Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
विकल्प
Will depend on the average wavelength
Will depend on the longest wavelength
Will depend on the shortest wavelength
Does not depend on the wavelength
उत्तर
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential will depend on the shortest wavelength.
Explanation:
The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon of emission of the electron when the photon incident on the metallic surfaces.
• The electrons emitted from the metallic surface due to the photoelectric effect are called photoelectrons.
• The rate of emission of photoelectrons depends upon the frequency or wavelength of the incident light.
• When higher frequency or lower wavelength light incident on the metallic surface, more photoelectrons will be emitted giving rise to the photocurrent.
• Stopping potential is the minimum potential required for the prevention of ejection of photoelectrons due to the low wavelength radiations.
• In the case of polychromatic light, the radiation with high frequency and low wavelength will contribute to the ejection of electrons.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
Photocurrent recorded in the microammeter in an experimental setup of the photoelectric effect vanishes when the retarding potential is more than 0.8 V if the wavelength of incident radiation is 4950 Å. If the source of incident radiation is changed, the stopping potential turns out to be 1.2 V. Find the work function of the cathode material and the wavelength of the second source.
The threshold wavelength of tungsten is 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(a) Explain why no photoelectrons are emitted when the wavelength is more than 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(b) What will be the maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected in each of the following cases
(i) if ultraviolet radiation of wavelength λ = 1.80 × 10-5 cm and
(ii) radiation of frequency 4 x 1015 Hz is made incident on the tungsten surface?
As the intensity of incident light increases ______
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The energy of a photon is 2 eV. Find its frequency and wavelength.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
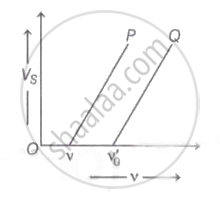
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
The threshold frequency for a certain photosensitive metal is v0. When it is illuminated by light of frequency v = 2v0, the maximum velocity of photoelectrons is v0. What will be the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons when the same metal is illuminated by light of frequency
v = 5v0?
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
When a surface 1 cm thick is illuminated by light of wavelength 'λ', the stopping potential is 'V0'. When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength '3λ', the stopping potential is `"V"_0/6`. The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected will be ______ eV when the light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. The work function of cesium = 1.9 eV.
For a given photosensitive material and frequency (> threshold frequency) of incident radiation, the photoelectric current varies with the intensity of incident light as:
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is ______.
By increasing the voltage in an electron diffraction tube, the radius of the diffraction rings will ______.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
