Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Cutoff wavelength of X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube depends on the
(a) target material
(b) accelerating voltage
(c) separation between the target and the filament
(d) temperature of the filament.
विकल्प
target material
accelerating voltage
separation between the target and the filament
temperature of the filament.
उत्तर
accelerating voltage
Cutoff wavelength (`lambda_min`) is given by `lambda_min = (hc)/(eV)`
Here,
h = Planck's constant
c = Speed of light
V = Accelerating voltage
e = Charge of electron
Clearly, a cutoff wavelength depends on accelerating voltage. It does not depend on the target material, separation between the target and the temperature of the filament.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why?
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(A) Radio waves.
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Name the waves of wavelength nearly 0.1 nm.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm Calculate the velocity of the wave.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Characteristic X-rays may be used to identify the element from which they are being emitted. Can continuous X-rays be used for this purpose?
The Kα X-rays of aluminium (Z = 13) and zinc (Z = 30) have wavelengths 887 pm and 146 pm respectively. Use Moseley's law √v = a(Z − b) to find the wavelengths of the Kα X-ray of iron (Z = 26).
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
Define the term "Intensity" in the photon picture of electromagnetic radiation.
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
State three properties of ultra-violet radiation similar to visible light.
A car is moving towards a high cliff. The car driver sounds a horn of frequency f. The reflected sound heard by the driver has a frequency 2f. If v be the velocity of sound, then the velocity of the car, in the same velocity units, will be:
The ozone layer absorbs
Following QN ∴ 14, the radiation force on the roof will be
The half-value thickness of an absorber is defined as the thickness that will reduce exponentially the intensity of a beam of particles by a factor of 2. The half-value thickness in (µm) for lead assuming X-ray beam of wavelength 20 pm, µ = 50 cm-1 for X-rays in lead at wavelength λ = 20 pm, is ______ µm.
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
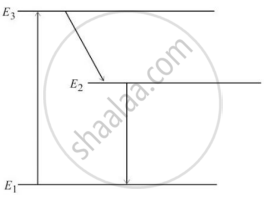
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
