Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following:
(i) Coulomb
(ii) Ohm
उत्तर
(i) Coulomb: It is the unit of charge.
(ii) Ohm: It is the unit of resistance. The resistance of a conductor is said to be 1 ohm, if 1 ampere current flows through it, when the potential difference across its ends is 1 volt.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the potential difference across the ends of a conductor is 220 V and the resistance of the conductor is 44 Ω (ohm), then the current flowing through is _________.
- 0.2 A
- 0.5 A
- 2 A
- 5 A
When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
Find the expression for the resistivity of a material and state the SI unit of resistivity.
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
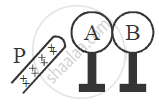
Two metallic spheres A and B kept on insulating stands are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod P is brought near the sphere A as shown in the figure. The two spheres are separated from each other, and the rod P is removed. What will be the nature of charges on spheres A and B?
The filament of a bulb takes a current 100 mA when potential difference across it is 0.2 V. When the potential difference across it becomes 1.0 V, the current becomes 400 mA. Calculate the resistance of filament in each case and account for the difference.
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
A metal rod of length 10 cm and a rectangular cross-section of 1 cm × `1/2` cm is connected to a battery across opposite faces. The resistance will be ______.
You are provided with a resistor, a key, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and few connecting wires. Using circuit components, draw a labelled circuit diagram to show the setup to study Ohm's law.
State the relationship between potential difference (V) across the resistor and the current (I) flowing through it. Also draw V-I graph, taking V on the X-axis.
