Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a cirde of radius 2 cm and touching a fixed circle of radius 3 cm with centre O.
उत्तर
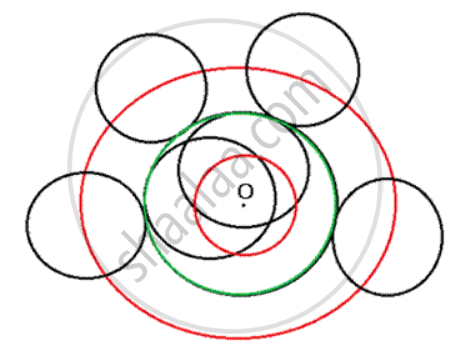
The locus is a concentric cirde (in red) of radius 1 cm if cirdes touch internally; and concentric cirde (in red) of radius 5 cm if cirdes touch externally.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use ruler and compasses only for this question. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm and mark two chords AB and AC of the circle of lengths 6 cm and 5 cm respectively.
(i) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from A and C. prove your construction.
(ii) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle that are equidistant from AB and AC.
Plot the points A(2, 9), B(–1, 3) and C(6, 3) on graph paper. On the same graph paper draw the locus of point A so that the area of ΔABC remains the same as A moves.
Construct a triangle BCP given BC = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm and ∠PBC = 45°.
- Complete the rectangle ABCD such that:
- P is equidistant from AB and BC.
- P is equidistant from C and D.
- Measure and record the length of AB.
A and B are fixed points while Pis a moving point, moving in a way that it is always equidistant from A and B. What is the locus of the path traced out by the pcint P?
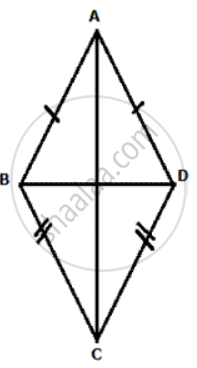
In given figure, ABCD is a kite. AB = AD and BC =CD. Prove that the diagona AC is the perpendirular bisector of the diagonal BD.
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The lorus of a point in rhombus ABCD which is equidistant from AB and AD .
Using a ruler and compass only:
(i) Construct a triangle ABC with BC = 6 cm, ∠ABC = 120° and AB = 3.5 cm.
(ii) In the above figure, draw a circle with BC as diameter. Find a point 'P' on the circumference of the circle which is equidistant from Ab and BC.
Measure ∠BCP.
Using only a ruler and compass construct ∠ABC = 120°, where AB = BC = 5 cm.
(i) Mark two points D and E which satisfy the condition that they are equidistant from both ABA and BC.
(ii) In the above figure, join AD, DC, AE and EC. Describe the figures:
(a) AECB, (b) ABD, (c) ABE.
Ruler and compass only may be used in this question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown, and be of sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment.
(i) Construct Δ ABC, in which BC = 8 cm, AB = 5 cm, ∠ ABC = 60°.
(ii) Construct the locus of point inside the triangle which are equidistant from BA and BC.
(iii) Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from B and C.
(iv) Mark as P, the point which is equidistant from AB, BC and also equidistant from B and C.
(v) Measure and record the length of PB.
Ruler and compasses only may be used in this question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown, and be of sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment.
(i) Construct a ΔABC, in which BC = 6 cm, AB = 9 cm and ∠ABC = 60°.
(ii) Construct the locus of the vertices of the triangles with BC as base, which are equal in area to ΔABC.
(iii) Mark the point Q, in your construction, which would make ΔQBC equal in area to ΔABC, and isosceles.
(iv) Measure and record the length of CQ.
