Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the locus for questions 1 to 13 given below:
1. The locus of a point at a distant 3 cm from a fixed point.
उत्तर
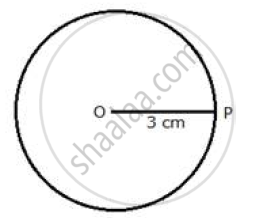
The locus of a point which is 3 cm away from a fixed point is circumference of a circle whose radius is 3 cm and the fixed point is the centre of the circle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In each of the given figures; PA = PB and QA = QB.
| i. | 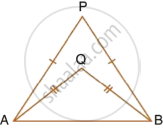 |
| ii. | 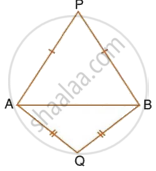 |
Prove, in each case, that PQ (produce, if required) is perpendicular bisector of AB. Hence, state the locus of the points equidistant from two given fixed points.
The given figure shows a triangle ABC in which AD bisects angle BAC. EG is perpendicular bisector of side AB which intersects AD at point F.
Prove that:
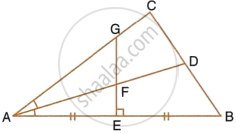
F is equidistant from A and B.
The bisectors of ∠B and ∠C of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at point P. Show that P is equidistant from the opposite sides AB and CD.
Draw an ∠ABC = 60°, having AB = 4.6 cm and BC = 5 cm. Find a point P equidistant from AB and BC; and also equidistant from A and B.
In the figure given below, find a point P on CD equidistant from points A and B.

Describe the locus of the centres of all circles passing through two fixed points.
The speed of sound is 332 metres per second. A gun is fired. Describe the locus of all the people on the earth’s surface, who hear the sound exactly one second later.
In the given figure, obtain all the points equidistant from lines m and n; and 2.5 cm from O.
By actual drawing obtain the points equidistant from lines m and n; and 6 cm from a point P, where P is 2 cm above m, m is parallel to n and m is 6 cm above n.
The bisectors of ∠B and ∠C of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect in P. Show that P is equidistant from the opposite sides AB and CD.
