Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
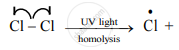
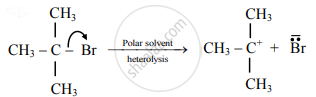
Distinguish between Homolysis and heterolysis.
उत्तर
| No. | Homolysis (Homolytic fission) | Heterolysis (Heterolytic fission) |
| 1. | The symmetrical breaking of a covalent bond in which each departing atom takes one electron from the bonding pair is called as homolytic fission. | The unsymmetrical breaking of a covalent bond in which one of the departing atoms retains the bonding pair is called heterolytic fission. |
| 2. | In this type of fission, the formation of free radicals (uncharged species) bearing unpaired electrons takes place. | In this type of fission, the formation of charged species called ions, like carbocation or carbonium ion takes place. |
| 3. |
The covalent bond between two atoms of the same element or two atoms having nearly the same electronegativity breaks in this manner.
|
The covalent bond between two atoms of the different elements or two atoms having different electronegativity values breaks in this manner.
|
| 4. | This takes place favourably in a nonpolar solvent. | This takes place favourably in a polar solvent. |
| 5. | Generally, reaction takes place at high temperature or in presence of UV light or peroxides. | Heterolysis takes place in solutions (polar condition). |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find out the most stable species from the following. Justify
`dot"CH","CH"_3-dot"CH" - "CH"_3,` \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 -\dot{C} - CH3}\\
|\phantom{.}\\\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
Find out the most stable species from the following. Justify.
`bar"C""H"_3, bar"C""H"_2"Br", bar"C""Br"_3`
Find out the most stable species from the following. Justify.
\[\ce{\overset{+}{C}H3, \overset{+}{C}H2Cl, \overset{+}{C}Cl3}\]
Draw a resonance structure of the following:
Phenol
Write true or false. Correct the false statement.
Heterolytic fission results in the formation of free radicals.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following statements are true with respect to electronic displacement in a covalent bond?
a. Inductive effect operates through π bond
b. Resonance effect operates through σ bond
c. Inductive effect operates through σ bond
d. Resonance effect operates through π bond
Choose the correct option.
Hyperconjugation involves overlap of ______ orbitals.
Choose the correct option.
The geometry of a carbocation is ______.
Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds by SNl reaction mechanism.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(I)}}{C6H5CH(C6H5)Cl}}\]
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(II)}}{C6H5CH2Cl}}\]
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(III)}}{C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Cl}}\]
Which of the following compound is highly reactive towards HCN?
Which of the following is TRUE for homolytic fission?
Identify the reagent used in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - Br ->[?] CH3 - CH2 - OH}\]
The best reagent for the following conversion is:
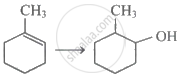
Which of the following alkyl groups shows maximum positive inductive effect?
IUPAC name of ![]() is ______.
is ______.
Which of the following represents a set of nucleophiles?
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α - carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α - carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen in each.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α - carbon in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{\oplus}{C}H -CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogens.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]