Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find out the most stable species from the following. Justify.
`bar"C""H"_3, bar"C""H"_2"Br", bar"C""Br"_3`
उत्तर
The most stable species from the given species is \[\ce{CBr^-_3}\].
This is because it contains 3 -Br atoms, which exhibits electron-withdrawing inductive effect. Carbanions are stabilized by - I inductive (electron-withdrawing) effect. The larger the number of –I groups attached to the negatively charged carbon atom, lower will be the electron density on the carbon atom and the higher will be its stability.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH_3 - CH_2 - \overset{⊕}{C}H-CH_2 - CH_3}\]
Draw a resonance structure of the following:
Phenol
Draw a resonance structure of the following:
Buta-1,3-diene
Distinguish between Homolysis and heterolysis.
Write true or false. Correct the false statement.
Homolytic fission involves the unsymmetrical breaking of a covalent bond.
Choose the correct option.
Hyperconjugation involves overlap of ______ orbitals.
Choose the correct option.
The geometry of a carbocation is ______.
Choose the correct option.
The delocalization of electrons due to overlap between p orbital and sigma bond is called _______.
Which of the following is NOT an electrophile?
Identify the reagent used in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - Br ->[?] CH3 - CH2 - OH}\]
The best reagent for the following conversion is:
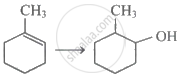
The most unstable free radical among the following is:
The overlap of σ-p orbitals is called ____________.
Which of the following represents a set of nucleophiles?
Which of the following is NOT an electrophile?
Which element among the following does form pπ - pπ multiple bonds?
Identify the group that exerts electron withdrawing resonance effect.
Arrange the following free radicals in order of decreasing stability.
- Methyl
- Vinyl
- Allyl
- Benzyl
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α - carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen in each.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{\oplus}{C}H -CH2 - CH2 }\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3
Identify the α - carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen in each.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α - carbon in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - \overset{\oplus}{C}H -CH2 - CH3}\]
Identify the α-carbons in the following species and give the total number of α-hydrogen.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH2 - CH3}\]
